- Echocardiogram - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003869.htm)
- About Echocardiogram - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/echocardiogram/basics/definition/prc-20013918?p=1)
- Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) - (http://www.heart.org/heartorg/conditions/heartattack/symptomsdiagnosisofheartattack/transesophageal-echocardiography-tee_ucm_441655_article.jsp)
What is an Echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram is an imaging test which uses sound waves to produce pictures of the heart. It helps to see the beating and pumping heart.
The echocardiogram provides a more detailed picture of the heart compared to x-rays. The pictures help in identifying the heart disease.
When is the Test Performed?
An echocardiogram is performed in the following circumstances.
- To evaluate the complete function of the heart.
- To determine the existence and to keep track of heart problems like
- Heart valve problems
- Arrhythmias (Heart Rhythm Disturbances)
- Heart murmurs (An extra sound during the heart beat)
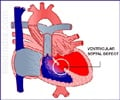
- Congenital heart defects (Heart problems from birth)
- Cardiomyopathies (Disease involving the muscle of the heart)
- Heart failure (Reduced pumping heart capacity)
- Infective endocarditis (Infection of the inner lining of the heart)
- Heart attack (Decrease in the blood supply to the heart)
- Pericardial diseases (Disease of the heart outer layer)
- Cardiac thrombus (Blood clot in the heart)
- Tumors in the heart (Extra unwanted growth)
- It is also performed before and after the treatment procedures, to see the effectiveness of the treatment.
Types of Echocardiogram
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE)
TTE is the most regularly performed echocardiogram. It is a non-invasive test. A sonographer conducts the test and a cardiologist interprets it. The sonographer applies gel on the chest and uses a device called a transducer with which he firmly presses over the chest to view the heart. The transducer releases high-frequency sound waves, picks the echoes of sound waves and converts them to electrical signals. The echocardiogram machine converts the electrical signals from the transducer and converts them into motion pictures of the heart.
In cases where the lungs, ribs or other body tissues block the sound waves and echoes, to produce the clear heart image, an intravenous contrast agent is useful to get the clear picture of the heart.
Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE)
Transesophageal echo helps to get detailed images of the heart. It is used to visualize the heart valves in detail. The throat is numbed before the procedure and drugs to relax the patient are given. A tube with the transducer which can generate the sound waves to collect the images is inserted through the throat into the esophagus (food pipe).
Doppler Echocardiogram
It helps to visualize the flow of blood in the heart and blood vessels. The measurement of the speed and the direction of the blood in the heart can be done with Doppler echo. Doppler technique is performed with TTE or TEE. It helps in detecting the blood flow-related problems and to
Stress Echocardiogram
In patients with heart conditions related to the coronary arteries, the blood supply to the heart decreases on physical exertion. In such cases, an echocardiogram is done at rest and after exercise stress on a treadmill testor after administering medication which makes the heart pump harder. The wall motion of the heart on echo helps to know the coronaries status. Wall motion abnormalities indicate coronary artery disease.
Three-dimensional Echocardiogram (3D Echo)
It is a non-invasive and safe test. It helps in assessing the cardiovascular function and cardiac anatomy. It has an improved accuracy over the 2D echo in assessing the left ventricular function, volume and the mitral valve area.
How is an Echocardiogram Done?
A technician or a cardiologist performs the test. The lights in the room will be dimmed during the procedure. After exposing the chest, a gel is applied to the skin, which helps in conducting the sound waves adequately. Using a transducer the sonographer presses on the chest and moves it over the chest for imaging the heart. The sonographer may ask you to breathe particularly and to roll to the left side for obtaining good images. The gel over the skin will be removed. You can do everything normally after the test.
What are the Potential Risks of Having an Echocardiogram?
Echocardiogram is a very safe procedure. There are no complications. The sound waves are not harmful, unlike the x-rays. TEE is also a safe procedure, but has risks very rarely. The complications of TEE are a sore throat for next 1-2 days and sometimes bleeding, infection of the esophagus.