- Functional magnetic resonance imaging - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/functional_magnetic_resonance_imaging)
What is Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)?
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging or fMRI is a safe, non-invasive diagnostic procedure used for measuring brain activity.
It is a newer technology that can measure the metabolic changes inside the brain and also the abnormalities which are not possible using other conventional imaging techniques.
What is the Difference Between MRI and fMRI?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the precursor of fMRI, which has been extensively used for studying anatomy of the brain. It can only capture the images of the brain. The ‘f’ in front of MRI stands for ‘functional’, which ideally means that the same technique can capture images when the brain is in action.
How Does fMRI Work?
The mechanism on which both the imaging techniques work is ‘Magnetic Resonance’. It is a phenomenon in which the atoms in the body emit electromagnetic radiation in response to a magnetic field.
MRI uses a magnetic field, radiofrequency waves to capture images of the brain. fMRI also uses the same but measures the blood flow inside the brain.
Several scientists had identified that blood flow is directly related to the brain activity. In 1990, a chemist named Linus Pauling first identified that when oxygen-rich blood was exposed to a magnetic field, it behaved differently compared to oxygen-deficit blood.
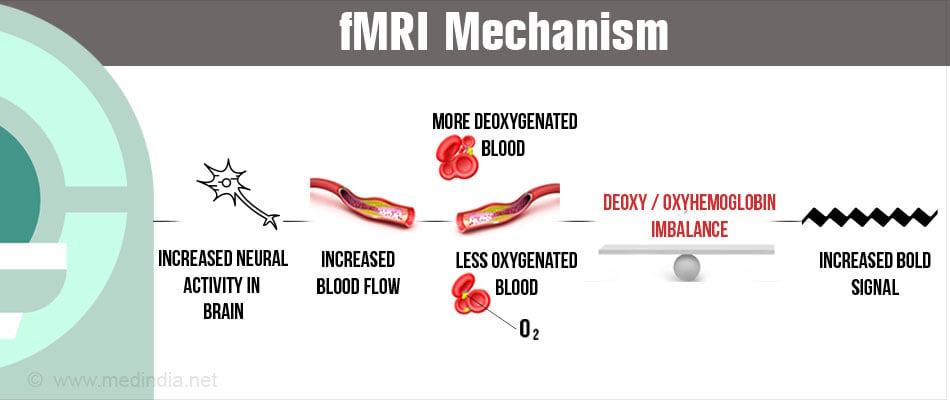
Active regions of the brain receive more oxygenated blood than less active regions. Therefore, fMRI can capture images of the active regions of the brain by measuring the blood flow, the volume of blood and the amount of oxygen used which is called as the Blood-Oxygen-Level-Dependant (BOLD) signal. Seiji Ogawa and Ken Kwong have been credited for using this discovery for imaging technique.
The fMRI scanner consists of a large cylindrical tube comprising of a very powerful electromagnet. It has a field strength of 3 Teslas (T), which is about 50,000 times greater than the earth’s field.
Generally, atomic nuclei are randomly aligned but under the influence of a magnetic field, they get aligned in the direction of the field. The fMRI measures the magnetic signal from hydrogen nuclei in water (H2O).
What are the Uses of fMRI?
fMRI is commonly used by physicians to analyze the functions of the brain. They perform this technique to:
- Study the structure of the brain
- Examine the effects of stroke, trauma or neurodegeneration on brain function
- Monitor the growth of brain tumors
- Plan surgical treatments for the brain
- Evaluate the regions of the brain involved in various functions such as thought, speech, movement and sensation

How to Prepare for an fMRI?
fMRI is a safe and a simple procedure which does not use any ionizing radiation. It can be performed on both inpatients and outpatients.
- fMRI is painless and requires no injections
- Before the technique, the radiologist may ask the patient to wear loose-fitting clothes or a gown
- If you have an allergy or undergone any recent surgeries, inform the radiologist or the nurse
- Women should inform physicians if they are pregnant
- One must remove all the jewelry, metal objects such as pins, pens, glasses and body piercings
- MRI exam is safe for people with metal implants, but not for people who have a cochlear implant, metal clips or metal coils placed within blood vessels and a pacemaker.
How is an fMRI Done?
The person will be placed on a movable examination table. The head of the patient is bolstered with braces to keep them still during imaging. Goggles or ear plugs will be given to measure audio-visual stimuli.
The person will be placed in the magnet of the MRI scanner and unlike MRI, the radiologist will ask the person to do certain activities such as looking at a picture, listening to sounds and answering simple questions.
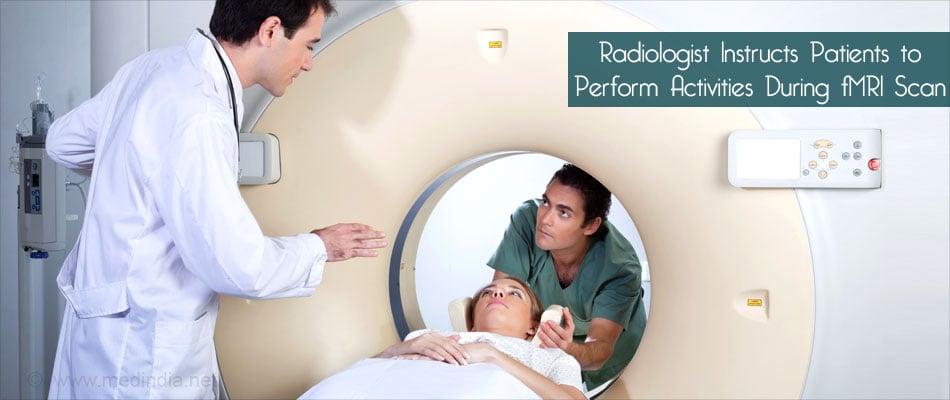
The radiologist can see, speak and hear the patient. A friend or a family member will be allowed inside the scan room. Each scan lasts for about 10 minutes.
When the patient performs a task, the neuronal activity in the brain increases and the fMRI captures the changes in the hydrogen ions. A computer then processes these signals, and a radiologist interprets the series of images generated.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of fMRI?
fMRI has several advantages namely,
- It is non-invasive and does not involve radiation.
- It produces excellent high-resolution images

- It is easy to use.
- The whole process can be completed in an hour
- It helps physicians to evaluate both the structure and functions of the brain
There are certain disadvantages of fMRI which include,
- It is expensive compared to other scans
- The patient has to stay still to capture clear images
- Patient’s movements can affect the quality of images