- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine 17th Edition.
- Stephen K. Frankel, Eugene J. Sullivan, Kevin K. Brown. Vasculitis: Wegener granulomatosis, Churg-Strauss syndrome, microscopic polyangiitis, polyarteritis nodosa, and Takayasu arteritis. Crit Care Clin 18 (2002) 855– 879.
About
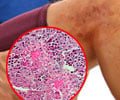
Microscopic Polyangiitis (MPA) is a vasculitis affecting small blood vessels. Patient is treated with cyclophosphamide and a corticosteroid.
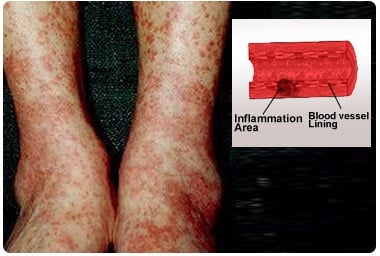
The patient may show general signs and symptoms like fever, muscle pain and weight loss. He may suffer from complications like kidney failure, bleeding in the lungs or perforation in the digestive system. Blood tests, imaging studies like x-ray and CT scan and biopsy of the affected organ are used to diagnose the condition. The blood level of a specific antibody called ANCA is high in patients with MPA. The patient is treated with drugs that suppress immunity like cyclophosphamide and corticosteroids.
MPA shares some common features with another vasculitis i.e. Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Patients with MPA develop kidney disease similar to Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Blood levels of ANCA are high is both conditions. However, unlike in Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis, accumulations of cells called granulomas are not seen in MPA. MPA affects the smallest blood vessels, while Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis usually affects the medium sized blood vessels. Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis often affects the upper airways. Upper airway disease is usually not seen in MPA.
MPA should also be differentiated from another vasculitis called Polyarteritis Nodosa. In MPA, very small vessels like capillaries, venules or arterioles are inflamed. These vessels are usually not affected in Polyarteritis Nodosa.