- Sahin C. Nasolabial Cyst. Case Rep Med. 2009; 2009: 586201. doi - (10.1155/2009/586201)
- Acar AH, Yolcu U, and Asutay F. Is Ultrasonography Useful in the Diagnosis of Nasolabial Cyst? Case Reports in Dentistry 2014, Article ID 678541, 3 page - (http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/678541)
What is Nasolabial Cyst?
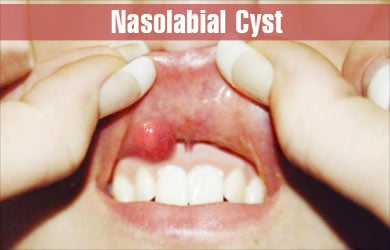
A nasolabial cyst, also called a nasoalveolar cyst or Klestadt`s cyst, is a soft-tissue swelling that occurs in the region between the nose and the upper lip. It is a problem that actually originates during fetal development within the uterus, but it usually manifests only in adulthood.
This cyst is non-odontogenic, that is, it is not formed by cells that go on to form the teeth. From the outside, it looks like a swelling under the skin, but it can be better appreciated under the upper lip from inside the mouth.
What are the Causes of Nasolabial Cyst?
Nasolabial cyst arises due to a developmental malformation during formation of the face. However, it appears as a swelling only in adulthood, usually between 40 to 60 years of age. The exact cause on how it originates is not known, though theories have been suggested. Trauma to the area could be a predisposing factor for the appearance of the cyst.
What are the Symptoms of Nasolabial Cyst?
Symptoms of nasolabial cyst are:
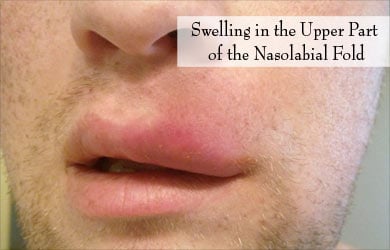
- Appearance of a small swelling under the skin of the face. The swelling is located in the region of the upper part of the nasolabial fold, the skin fold that extends from the nose to the angle of the mouth. Thus, the swelling is closer to the nose than the lip. The swelling may distort the face, pushing the lip and the nasal ala outwards.
- The cyst usually occurs on one side, though in some cases, it may be present on both the sides.
- The swelling is soft to firm and painless. It may gradually increase in size.
How to Diagnose Nasolabial Cyst?
There are several other cysts beside nasolabial cysts in the region of the face, which should therefore be differentiated from these cysts. Diagnosis is made based on:
- History from the patient
- Physical examination of the inside of the mouth, which will reveal the presence of a pink or bluish cyst.
- X-ray examination, to differentiate it from other swellings in this region. Nasolabial cysts however are not obvious on x-ray. Changes in the underlying bone may be noted if it undergoes erosion. CT scan, and MRI are the other commonly used radiological tests.
- Biopsy can be performed after surgical removal of the cyst to confirm the diagnosis.
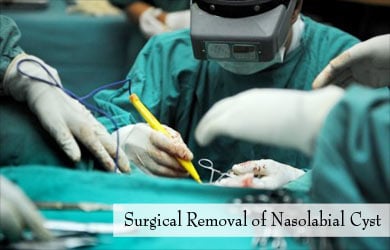
How do you Treat Nasolabial Cyst?
Nasolabial cysts are treated by:
- Surgical removal of the entire cyst
- Injection of sclerosing substances into the cyst to harden the cyst
- Marsupialization of the cyst using a nasal endoscope. In this procedure, the cyst is opened up and kept open so that it drains out freely.