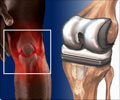
What is Orthopedic Surgery?
Orthopedic surgery, also referred to as orthopedics, is a branch of surgery that deals with health conditions and diseases that affect the musculoskeletal system, including the joints, bones, ligaments, tendons, muscles and nerves. Specialists in orthopedic surgery are known as orthopedic surgeons and they use both surgical and non-surgical methods of treatment to provide relief to patients suffering from sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections and other health conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system.
Orthopedic surgeons treat patients of all age groups, from newborns and infants with congenital conditions and deformities like scoliosis to aged adults with degenerative diseases and joint problems. Many celebrity physicians that you see on the cricket or soccer pitch are also orthopedic specialists, as athletes and sportsmen are among the most common younger patients who require orthopedic treatments.
Orthopedic surgeons often work side by side with general surgeons, especially in emergency care. Orthopedic surgeons help with the following areas:
Diagnosis – the diagnosis and detection of musculoskeletal disorders with tools like x-rays and blood tests.
Treatment – orthopedic surgeons ususally deliver surgical care but treatment can also be purely medical.
Rehabilitation – the scope of orthopedics is not restricted to diagnosis and treatment, but is also concerned with aftercare and rehabilitation. Orthopedic surgeons recommend physical activities, lifestyle changes and physiotherapy with the specific aim of improving mobility, restoring strength and functionality to the affected part of the body.
Although orthopedic surgeons treat a very wide clientele, they also do have specialization in certain areas such as pediatric orthopedics or sports surgery.
Types of Orthopedic Surgery / Most Common Orthopedic Surgeries
Orthopedists provide patients with a wide range of treatments, not all of which are necessarily surgical. Some of the procedures that require orthopedic specialists include traction, amputation, limb reconstruction and joint replacement surgeries. Orthopedic surgeons are often involved in routine emergency care procedures to deal with fractures, broken bones, strains, sprains and joint dislocation, while their specialized care is even more crucial to procedures like arthroscopic surgery, arthroplasty, kneecap removal and so on.
The most common orthopedic surgery procedures include the following:
Arthoscopy – This is a keyhole surgery, which means that it is a minimally invasive technique, used to investigate, diagnose and sometimes even treat problems that affect the joint like damaged joint tissue. The procedure is conducted by using an arthroscope, which is a specialized endoscope that is inserted into the joint via small incisions.
Repairing bone fractures – Orthopedic surgery is often used to treat fractures for internal fixation by first correctly repositioning the bone/bone fragments, so that they are returned to the normal alignment. Orthopedic implants like plates, screws, nails and wires are then used to secure the damaged bones. This method is commonly used when dealing with fractures like a broken rib, leg, hip, ankle or collar bone.
Arthroplasty – This is a type of orthopedic surgery that is critical to the practice of joint replacement. Arthroplasty is commonly used to replace whole joints such as in knee replacement or hip replacement surgery.
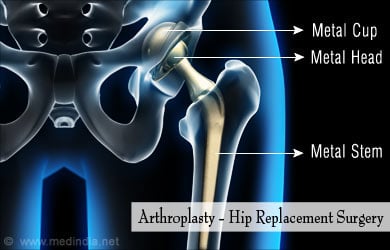
Repair of tissue damage – This includes treatment for damaged muscles, torn ligaments or tendons. While strains and sprains are treated with rehabilitative care, more serious tears of ligaments or tendons require surgery.
Corrective surgery – Orthopedic procedures are often used to correct structural abnormalities or deformities of the musculoskeletal structure, especially the spine and limbs. This is necessary when the condition affects mobility, limits function or poses long-term problems if not dealt with. Osteotomy and fusion surgery are two such orthopedic surgical procedures. Osteotomy involves cutting and repositioning the bone to correct deformities, while fusion surgery, as the name suggests, involves welding or fusing bones together so that they heal as a single solid bone.
Preparation for Orthopedic Surgery
Choosing the most suitable orthopedic specialist is the first step towards getting the best possible treatment. Your family physician, who is well acquainted with you, would be best able to assist in recommending and choosing an orthopedic surgeon based on your specific requirements. Before any surgical procedure is recommended you will need to undergo a number of tests and diagnostic procedures that could include imaging tests like x rays, computed tomography or CT scans, magnetic resonance imaging or MRI, blood tests, electrocardiogram and arthroplasty. This will help your doctors and orthopedic specialists make a better informed decision on the corrective procedure that is required.
Before a final decision is taken with regard to orthopedic surgery you will be asked to undergo a period of rest for the affected area. It is imperative that you comply with the recommendations of your health care provider.
Patients can also donate some of their own blood prior to the procedure. This blood can be held in reserve if there is considerable loss of blood in a major surgery such as knee replacement surgery.
Rehabilitation after Orthopedic Surgery
Rehabilitation is one of the most important aspects of orthopedic care as the entire purpose of orthopedic surgery and treatment is to restore normal function to the affected musculoskeletal structure. Recovery is often the toughest part however, as it is often slow and requires a great deal of effort. Your doctors will work closely with physiotherapists to ensure that you receive suitable treatment and care to promote and restore the full range of movement to the affected area.

The effectiveness and duration of rehabilitative therapies will vary greatly, depending on various factors, such as the general health and activity levels of the patient, the age of the patient and presence of other health conditions. This said, there are certain concerns that are common to almost all patients after undergoing orthopedic surgery. These include:
Swelling and inflammation – This is a common problem that affects the joint after surgery. These symptoms or effects, to be more precise, will last for several weeks and patients need to use coping strategies. Keep the affected joint elevated slightly. While reclining or lying in bed for example, swelling in the knees or ankle should be addressed by keeping the leg elevated on two to three pillows. This should be done for intervals of half an hour at a time, at least thrice a day. Bruising and blistering on the site of surgery is not uncommon and is not a cause for concern. If you experience pain in addition to swelling, particularly in the calf, there is a possibility of a blood clot having formed and you should contact your health care provider immediately.
Pain relief – The use of cold compresses can help control pain and swelling to some extent. Try to apply an ice pack to the surgical site for around twenty minutes at a time, several times in a day.
Pain medication – Pain is an unavoidable side effect from almost any and all surgical procedures, with orthopedic surgery being no exception. Pain medications are therefore routinely prescribed and you should make it a point to follow the dosage and instructions as prescribed by your orthopedic doctor.
Cautionary Advice: Lifestyle choices play a central role when examining the outcome of any orthopedic surgical procedure. While treatment will help to correct a problem, recovery is not possible unless patients cooperate fully and make an effort to follow recommendations. A regular exercise regime is absolutely vital to ensuring the fitness and health of the muscles, ligaments and tendons or the bones around the joint.
- Formulate an exercise plan along with your physician, orthopedic surgeon and physiotherapist.
- Ideally, exercises should encourage mobility and use of the joint but should exclude any kind of impact activities like running or sports like tennis that could put a great deal of stress on the joint.
- Similarly, it is advisable to avoid activities with a high risk of injury such as downhill skiing or ice skating.
- Low-impact activities include walking on a treadmill, using a stationary bike, swimming, sports like bowling, golf and also activities like gardening and dancing.
- Seek support from counselors and support groups.
- Inflammation and swelling of surgery site
- Infection of the surgery site
- Damage to nerves, soft tissue, or even the spinal cord
- Formation of blood clots
- Scar formation

Adhere strictly to your doctor’s prescription even if you feel that you do not need pain medications! Not all of those medications are prescribed for pain and antibiotics are commonly used to prevent infection in the surgery site.
Risks Associated with Surgery
All surgical procedures are associated with some kind of risk. Excess blood loss, infection and allergic reactions to anesthesia are some important concerns when going into any surgery, but these procedures are only conducted after a thorough risk assessment. When dealing with orthopedic surgery, some specific risks include: