What is Synovectomy?
Synovectomy is a surgical procedure in which a portion or whole of the synovial membrane lining the joint is removed.
The synovial membrane (also known as synovium) is a connective tissue that lines the inner surface of the joints, tendons and bursae. It helps in the lubrication and free movement of the joints by secreting synovial fluid. When the synovial membrane gets inflamed, it is known as synovitis.
Why is it done?
The following are a few conditions where synovectomy is done.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: There is an excessive synovial growth in the joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. If the DMARDS (disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs) do not improve the condition, then synovectomy is an option.
- Synovial chondromatosis: It is a form of arthritis where calcifications form in the synovium. In patients with synovial chondromatosis, synovectomy is useful.
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis: There is an excess growth and inflammation of the synovium in patients with pigmented villo-nodular synovitis. Synovectomy provides relief in these patients.
- Hemophilia: Hemophilia is a bleeding disorder. The patients bleed into their joint (hemarthrosis) without any external cause. Repeated episodes of bleeding can lead to chronic joint edema and disability. Synovectomy helps in improving the joint function by decreasing the bleeding from the thickened synovium.
- Septic Arthritis: In patients with joint infection, synovectomy is useful.
- Psoriatic arthritis: It is seen in patients with psoriasis. Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic and progressing condition. It causes swelling and pain of the joints. Synovectomy helps to relieve the symptoms when there is no improvement with medications.
What are the Contraindications for Synovectomy?
Synovectomy is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Local skin infection
- Radiological synovectomy is contraindicated in pregnant and breast feeding mothers
- Extensive joint disability
- Osteoarthritis with severe joint destruction
What are the Types of Synovectomy?
- Chemo synovectomy: It uses drugs like osmic acid (a strong caustic agent) that are injected into the affected joint space.
- Surgical: Surgical synovectomy is of two types. It can be performed by an open procedure or by a minimally invasive procedure on a joint known as arthroscopy or keyhole surgery.
- Radio synovectomy: It is a type of synovectomy where radioactive substances like Yttrium-60, Erbium-169, dysprosium-165 or rhenium-186 are injected into the affected joint space. It is performed in mild synovitis cases and in children with hemophilia who develop synovitis due to bleeding into their joints.
How do you Prepare before Synovectomy?
Careful patient evaluation is required before a decision to perform surgery is made.
History and physical examination: A thorough history and examination of the affected joint are made to evaluate the degree of damage, pain and discomfort and range of movement.
Imaging studies: The involved joints should be classified radiologically through the following tests for a better understanding of the pathology and confirmation of the diagnosis.
- X-ray: It is a very simple radiological test which is easily available. It provides the images of the affected joints.

- MRI: You will be tested in a narrow tube which makes loud sounds during the test. To decrease the sound exposure, ask for earplugs before the test. It provides high resolution images of the joints.
- Ultrasonography: It is a test where a small probe is put against the skin and moved over the skin. It helps to view the soft tissues of the body.
- Scintigraphy: It is a test where you will be given a radiotracer through oral, intravascular or inhalational route. The radiotracer reaches the abnormal sites that are targeted. The images are created using a special camera and a computer.
Routine Preoperative Tests:
Regular tests performed a few days before any elective surgery are done. The following are the tests -
- Complete blood picture to check the hemoglobin level and blood counts.
- Bleeding time and clotting time: Abnormal bleeding or clotting can cause an increased blood loss during surgery. So the clotting time and bleeding time are essentially checked before any surgery.
- Virology screen: Viral tests for Hepatitis B and HIV are necessary before surgery, so that the doctor can take necessary precautions.
- Blood grouping and typing: Blood grouping and typing should be done before surgery because it will be helpful if there is excess unexpected blood loss during surgery.
- Urine test: A complete urine examination is essential.
- Renal function test: Blood levels of creatinine and urea help to detect the kidney function.
- Liver function test: Serum proteins levels, alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, alkaline phosphate and bilirubin levels will give a picture of the liver function.
- Chest X-ray: Chest x-ray helps to find lung and heart problems.
- Electrocardiogram: It is a record of the electrical activity of the heart which helps to assess the heart function.
The following are a few instructions given 2 weeks before the surgery
- You will be asked to avoid drugs which make it hard for the blood to clot, like aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen.
- You will be asked to avoid alcohol and tobacco smoking.
- You will have to visit the anesthetist in the hospital or health center with all the preoperative investigations and get checked to ensure that you are fit to receive anesthesia.
- You will be asked to let your doctor know all your concerns and queries before the surgery.
- You will be asked to come on time on the day of surgery or a day before.
A day before surgery: You will be asked to fast for 8- 10 hours before the surgery. You may be prescribed a sleep medication on the night before surgery.
On the day of surgery: Take the tablets you are advised to take on the day of surgery but only with a sip of water.
What Happens During the Surgery?
You will be taken to the waiting area near the operation theater before surgery, where you may have to wait until the operation theater is ready to start your procedure.You will then be shifted to the operation theater.
The environment in the operation theater may be scary. There will be an overhead light and an anesthesia machine near the head end of the operation table. There will be monitors that record your oxygen level, vitals and ECG. The sounds from the monitors may sometimes be disturbing. You may be given some sedation to calm you down.
The type of anesthesia for patients undergoing synovectomy varies. One of the following types of anesthesia will be used
- Local anesthesia: The skin near the joint to be operated is injected with the drug to block the sensation. You will be awake during the procedure.
- Regional anesthesia: In the case of lower limb joints, spinal anesthesia is given where the drug is injected in between the lumbar vertebrae. The lower body will become numb and you will be awake during the procedure.
- General anesthesia: For general anesthesia, you will be given a medication through an intravenous line. You will then fall asleep. Endotracheal tube will be inserted and inhalational anesthetic agents will be given.
Operative procedure:
Synovectomy can be done by either open method or an arthroscopic method.
Open synovectomy: In this method of synovectomy skin incision will be given near the joint, and the soft tissue will be carefully dissected. The abnormal synovial membrane layer will be identified and excised. Any loose bodies in the joint cavity and debris will be removed. Any adhesions or scar tissue has to be excised too. The soft tissue and the skin will be sutured back. The wound will be covered with compressive dressing.
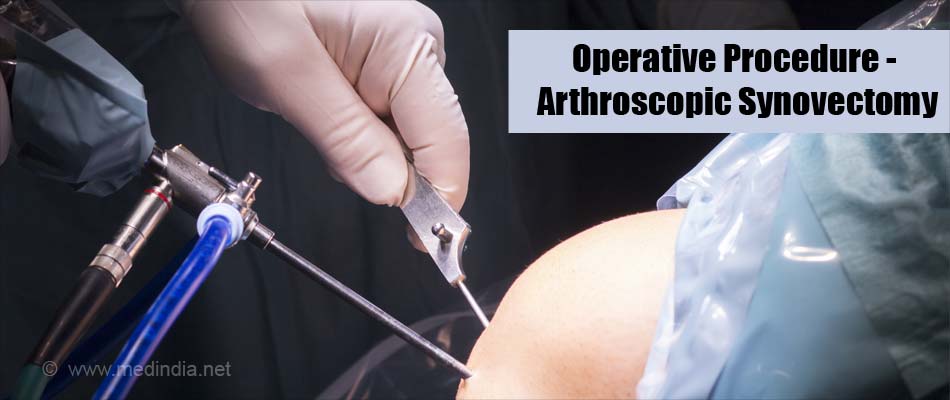
Arthroscopic synovectomy: In this method, 3-4 small incisions will be given on the skin near the joint. Through one incision, the surgeon inserts a thin tubular instrument called the arthroscope with a camera at its end, which helps to view the joint interior on the screen. Through the remaining incisions, the small surgical instruments that help to cut and remove the excess synovium will be introduced. Bleeding is controlled with electrocautery. The skin incisions will be sutured once the synovectomy is done. A compressive dressing is applied over the wound.
What Happens After the Synovectomy?
- After the procedure, you will be transferred to the recovery room to be monitored for some time before being shifted to your room.
Recovery after Synovectomy
- Your vital signs such as blood pressure and heart rate will be carefully monitored in the recovery room and once they are stable you will be shifted to your room.
- Your doctor will prescribe pain medications after the surgery.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Prophylaxis: If the surgery is on the legs and if you are unable to walk, you will be given a DVT prophylaxis.
- Post-operative diet: You may be discharged on the day of the procedure or one day after the procedure. You will not be given food and water soon after surgery if general anesthesia was used during the operation. Once your bowel recovers, you will be given drinks and food gradually after 4-6 hrs.
- Joint exercises – Exercises to regain muscle strength and joint mobility will be taught 24-48 hours after surgery and once the suction drain is removed. These have to be continued at home.
What are the Risks and Complications of Synovectomy?
Complications due to surgery can be anesthesia-related or due to the surgery itself. The following are a few complications:
- Bleeding into the joint: The injury to a blood vessel during the procedure can cause bleeding into the joint.
- Infection in the joint: After the procedure, there is a chance of infection of the joint. The patients will usually be given antibiotics peri-operatively and also for a few days at home to avoid such complications.
- Damage to the ligaments and cartilage: Injury to the cartilage and ligaments around the joint space can occur during the procedure.
- Joint stiffness: It occurs more in patients with open synovectomy than arthroscopic method. Physical therapy will be helpful in patients with joint stiffness.
- Damage to a blood vessel or nerve: During the operation, injury to the blood vessel and the nerve may occur. Injury to the blood vessel will cause bleeding and injury to the nerve can cause numbness, loss of sensation or muscle weakness depending on which nerve is involved.
- Blood clots in leg or lung: If the patient is mostly in the bed after the procedure it can cause blood clots in the leg and which can travel to the lung. Necessary measures will be usually taken by the surgeons, in the patients with risk for a blood clot.
Instructions following discharge:
- You will need to take oral pain medications to alleviate joint pain and inflammation.
- Rest, compression and elevation of the joint are necessary to decrease the pain and swelling.
- Slings or crutches should be used when necessary for the comfort and to protect the joint.
- Your doctor will suggest physical therapy after the procedure to improve the muscle strength and the joint function.

Follow-ups:
Your doctor or his team member will let you know about the follow-up visits before the discharge from the hospital. The first visit may be in a week or ten days for removal of sutures and for evaluating the joint recovery.