- Physiology, Gallbladder - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482488/)
- Gallstones (Cholelithiasis) - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459370/)
- Nutritional approaches to prevention and treatment of gallstones - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19803550/)
- Healthy Dietary Pattern Reduces Risk of Gallstones: Results of a Case-Control Study in Iran - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9188884/)
- Fruits and vegetables consumption and the risk of gallstone diasease - (https://journals.lww.com/md-journal/fulltext/2019/07120/fruits_and_vegetables_consumption_and_the_risk_of.64.aspx)
- Risk Factor of Dietary Habit with Cholelithiasis - (https://e-journal.unair.ac.id/JCMPHR/article/view/27931)
- Diet and Gallstone - (https://www.intechopen.com/online-first/1144920)
- Anti-gallstones Diet: What Foods to Eat and What to Avoid - (https://health.umms.org/2022/09/30/anti-gallstones-diet/)
- Diet-quality scores and the risk of symptomatic gallstone disease: a prospective cohort study of male US health professionals - (https://academic.oup.com/ije/article/47/6/1938/5127270)
What are Gallstones?
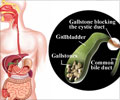
The gallbladder is a small organ that resembles in size and shape of pear fruit and lies in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, attached to the under surface of the liver. It is a part of the biliary tract, or biliary system, that includes other organs such as the liver and pancreas. The gallbladder plays an important role in storing and concentrating bile, a fluid that is required for digesting dietary fats, excreting cholesterol, and exhibiting antimicrobial activity(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Physiology, Gallbladder
Go to source).
Cholelithiasis is the medical term for stones in the gallbladder. When the gallbladder doesn’t completely drain the bile, it precipitates into sludge, resulting in stones. The gallstones are composed of cholesterol, bile, and bilirubin. The common symptoms of gallstones include pain in the right upper abdomen, nausea, vomiting, and radiating pain from the epigastrium to the mid-back.
Gallstones are classified as pigmented stones or cholesterol stones. About 80% of the stones reported are cholesterol stones. The risk factors for gallstones include obesity, female gender, aging, metabolic syndrome, prolonged fasting,
Gallstones (Cholelithiasis)
Go to source).
The space below will shed light on healthy foods for the gallbladder and dietary advice for gallstones.
Role of Diet in Gallstone Formation
Diet plays a crucial role in understanding the prevention and treatment strategies for gallstones. The dietary factors that scale up the risk of gallstones are cholesterol, trans fatty acids, saturated fats, and refined sugar. Consuming a vegetarian diet has been found to be associated with reduced risk of gallstones formation(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Nutritional approaches to prevention and treatment of gallstones
Go to source).
A study that compared the dietary intake of patients with gallstones and controls revealed two types of dietary patterns. The healthy dietary pattern that included a higher consumption of vegetables, fruits, legumes, fish, nuts, and vegetable oil and a lower consumption of hydrogenated fats and salt expressed an inverse association with gallstones. This, in turn, can be considered gallbladder-friendly food. Whereas, the unhealthy dietary pattern that included excess intake of artificial fruit juice, refined grains, sweets, desserts, red meat, processed meat, snacks, and pickles was directly linked to the risk of gall bladder diseases(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Healthy Dietary Pattern Reduces Risk of Gallstones: Results of a Case-Control Study in Iran
Go to source).
What are the Foods to Eat for Gallstones?
The gallstone diet plan should comprise a high intake of fruits and vegetables. Evidence has reported the protective effects of fruits and vegetables against gallstone formation. Vegetables and fruits rich in fiber reduce transit time in the intestine and bring down total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels. This occurs due to its stimulating effect on bile acid excretion and decreases the hepatic synthesis of cholesterol(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Fruits and vegetables consumption and the risk of gallstone diasease
Go to source).
Foods rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) and omega-3 fatty acids, like polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are beneficial for treating gallstones. The mechanism behind the protective effect of omega-3 PUFA that augments nucleation time and cholesterol saturation index. It alters the cholesterol metabolism, thereby reducing biliary cholesterol and protein concentrations. Nuts, fish, and whole grains are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids, and MUFA can be found in olive oil(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Risk Factor of Dietary Habit with Cholelithiasis
Go to source). Dietary fish oil supplementation was found to be beneficial for the gallbladder. It helped reduce cholesterol saturation, cholesterol crystallization, bile protein concentration, and triglyceride levels(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diet and Gallstone
Go to source).
Nuts are rich sources of unsaturated fatty acids and dietary fiber and are gallstone-friendly. Consuming nuts at least five times a week or more has a positive impact on lipoprotein and cholesterol profiles(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Risk Factor of Dietary Habit with Cholelithiasis
Go to source, 7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diet and Gallstone
Go to source).
Whole grains like whole wheat, brown rice, oats, millet, low-fat dairy products, and lean cuts of meat can be consumed as well(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Anti-gallstones Diet: What Foods to Eat and What to Avoid
Go to source).

What are the Foods to Avoid for Gallstones?
Foods to be avoided when following a gallstone diet plan include:
- Refined carbohydrates
- Saturated & trans fats
- Red & processed meats
- Sugary foods
- Fried foods
- Full-fat dairy products(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Anti-gallstones Diet: What Foods to Eat and What to Avoid
Go to source)
The impact of dietary fats on cholelithiasis has been extensively researched and is associated with adverse effects.High-carbohydrate foods, refined sugars, and refined carbohydrates like white flour, refined grains, baked products like cookies, cakes, candies, chocolates, and more increase energy intake and impart negative effects on the gallbladder(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diet and Gallstone
Go to source).

Foods to Eat to Prevent Gallstones
Mediterranean and DASH diets have been studied to manifest favorable effects. These dietary patterns comprise food groups such as vegetables, fruits, nuts, legumes, whole grains, low-fat dairy products, fish, and foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids(9✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diet-quality scores and the risk of symptomatic gallstone disease: a prospective cohort study of male US health professionals
Go to source).
Coffee or caffeine intake has shown protective effects as well. Moderate coffee consumption is known to increase enterohepatic circulation of bile, stimulate cholecystokinin release and gallbladder movement, and inhibit absorption of gallbladder fluids and the crystallization of cholesterol in bile(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Risk Factor of Dietary Habit with Cholelithiasis
Go to source).
Certain nutritional supplements that promote a healthy gallbladder include vitamin C, lecithin, soy, and iron(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Nutritional approaches to prevention and treatment of gallstones
Go to source). Ensuring adequate intake of phenolic compounds like flavonoids, lignans, phenolic acids (like hydroxycinnamic, hydroxybenzoic, and hydroxyphenyl acetic acids), and tyrosol helps in the prevention of gallstones.
Takeaway
Adapting healthy lifestyle habits structures a long-term prevention plan for gallstones. Along with eating nutritious foods, supplementary factors like staying physically active, consuming alcohol in moderation, and maintaining a healthy body weight are known to be beneficial in uplifting gallbladder health and preventing gallstones(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Risk Factor of Dietary Habit with Cholelithiasis
Go to source).