Methotrexate Medication Information
Learn everything you need to know about Methotrexate-pronunciation, uses, dosage guidelines, indications, and when to take or avoid it.
Get up-to-date information on side effects, precautions, warnings, and proper storage to ensure safe usage.
Explore Methotrexate brand names commonly used in India and internationally, along with detailed pricing information. Consult your healthcare provider for tailored medical advice.
Generic Name : Methotrexate Pronunciation : meth'' oh trex' ate ICD Code : Y45.4 Therapeutic Classification : AntirheumaticsBrand Names or Trade Names of Methotrexate
India :
Other Name(s) of Methotrexate
AmethopterinWhy is Methotrexate Prescribed? (Indications)
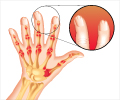
This medication is an antimetabolite, curative in choriocarcinoma (cancer of the tissue that normally would develop into placenta). It is also used in other cancers like blood, breast and lung cancers. It is also used to suppress immunity in conditions such as psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis.When should Methotrexate not be taken? (Contraindications)
It should not be administered during breast feeding. It should also not be used in patients allergic to the drug, pregnancy, liver disease, in alcoholics, people with low blood counts or decreased immunity.What is the dosage of Methotrexate?
Oral Burkitt's lymphoma- 10-25 mg/day for 4-8 days, repeat after 7-10 days.Oral & IMChoriocarcinoma(Ectopic Pregnancy)- 15-30 mg/day for 5 days, repeat after an interval of at least 1 week for 3-5 courses.
Mycosis fungoides- 2.5-10 mg/day to induce remission.
Rheumatoid arthritis- 7.5 mg once weekly, adjust if needed. Up to 20 mg/wk.
Crohn's disease- 12.5-22.5 mg once weekly for up to 1 year.
PO/IV/IM- Psoriasis- 10-25 mg once wkly, adjust subsequent doses if needed.
IV- Osteosarcoma- 12-15 g/m2 as infusion, followed by folinic acid.
Breast cancer 10-60 mg/m2 often with cyclophosphamide and fluorouracil. Advanced lymphosarcoma Up to 30 mg/kg, followed by folinic acid rescue. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia Maintenance: 2.5 mg/kg every 14 days.
How should Methotrexate be taken?
It comes as a tablet to take by mouth, with or without food.It also comes as a solution for injection to be administered by a healthcare provide into a large muscle.What are the warnings and precautions for Methotrexate?
•Caution should be exercised in patients with liver or kidney problems, blood disorders, diarrhea, and stomach problems.• If vomiting or diarrhea occurs, you will need to take care not to become dehydrated.
• It may cause liver or kidney impairment, bone marrow depression, ulcerative disorders of the GI tract.
• Avoid become pregnant while taking this medication.
• Monitor hematological, renal and hepatic function and GI toxicity regularly.
• Avoid drinking alcohol while you are taking this medication.
What are the side effects of Methotrexate?
Central Nervous System- Dizziness, fatigue, headache, language disorder, weakness, paresis, convulsions, destruction of the myelin sheaths (IV after cranio spinal irradiation), inflammation of the arachnoid (a covering of the brain), transient paresis, nerve damage.Skin- Redness of the skin, rashes, itching, loss of hair, hives, photosensitivity, pigmentary changes, skin discoloration, dilatation of blood vessels, acne, furunculosis, aggravation of psoriasis by ultraviolet light, severe allergic reactions.
Eye and ENT- Blurred vision, inflammation of the gums, inflammation of pharynx.
Gastrointestinal- Nausea, vomiting, enteritis, mouth ulcer, diarrhea, abdominal distress (common), loss of appetite, blood in vomit, blood in stool, GI ulceration and bleeding.
Genitourinary- Renal failure, blood contains excess amount nitrogen, inflammation of the urinary bladder, blood in urine, severe kidney disease, reproductive disorders, infertility, abortion, fetal defects.
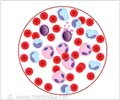
Blood- Deficiency of all three blood cell types, bone marrow depression, anemia, bleeding, presence of bacteria in the blood (septicemia).
Liver- Elevated LFTs (liver function test), liver damage.
Respiratory- Deaths from interstitial pneumonia, chronic interstitial obstructive lung disease.
Miscellaneous- Malaise, chills, fever, lower resistance to infections, joint pain, muscle pain, diabetes, osteoporosis, allergic reactions, sudden death.