Oxytocin Medication Information
Learn everything you need to know about Oxytocin-pronunciation, uses, dosage guidelines, indications, and when to take or avoid it.
Get up-to-date information on side effects, precautions, warnings, and proper storage to ensure safe usage.
Explore Oxytocin brand names commonly used in India and internationally, along with detailed pricing information. Consult your healthcare provider for tailored medical advice.
Generic Name : Oxytocin Pronunciation : ox-i-TOE-sin ICD Code : Y42 Therapeutic Classification : HormonesBrand Names or Trade Names of Oxytocin
India :
International :
Pitocin
Why is Oxytocin Prescribed? (Indications)
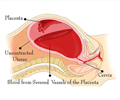
This medication is a uterine stimulant, prescribed for the initiation of uterine contractions and induction of labor in women as well as stimulation of contractions in cases where the uterus does not contract enough during labor. It is also used to help abort the fetus in cases of incomplete abortion or miscarriage, and control bleeding after childbirth. It may be used for breast engorgement.When should Oxytocin not be taken? (Contraindications)
This medication is contraindicated in cases where there is Cephalopelvic disproportion(CPD) (when a baby’s head or body is too large to fit through the mother’s pelvis); abnormal presentation of the fetus, excessive amniotic fluid; in women who have had multiple pregnancies, previous caesarian section or other uterine surgery; hyperactive or hypertonic uterus, uterine rupture; in cases where vaginal delivery is contraindicated (such as invasive cervical cancer, active genital herpes, prolapse of the cord, cord presentation or total placenta previa); fetal distress where delivery is not imminent; severe pre-eclamptic toxaemia (pregnancy induced high blood pressure).What is the dosage of Oxytocin?
IV- The recommended dose is 1 to 2 mU/min. Dosage should be adjusted at half an hour to hourly intervals. Max 32 mU/min.Postpartum haemorrhage: 10 to 40 mU by infusion at a rate to control uterine atony.
Adjunct in abortion: The recommended dose is 10 to 20 mU/min, max 30 IU.
How should Oxytocin be taken?
It is usually administered as an infusion at you doctor's office, hospital, or clinic. It is also available as a nasal spray.What are the warnings and precautions for Oxytocin?
•Stop the drug immediately if the uterus contracts excessively or the fetus is in distress.Intra muscular administration is not regularly used due to unpredictable effects of this medication.
Do not use it for prolonged periods in resistant uterine inertia, severe pre-eclampsia (hypertension), or severe CV disorders, hyper hydration.
Monitor neonates and mother’s heart rate, maternal BP and uterine motility, fluid intake and output during treatment.
What are the side effects of Oxytocin?
Genitourinary- Rupture of uterus, increased tone of uterine muscle.Fetus or neonate- Jaundice; abnormal heart rhythm, slow heart beat, brain, brain damage, seizure, eye bleeding, low Apgar score. (Activity, Pulse, Grimace, Appearance, and Respiration).
Mother- Low blood pressure, fast heart rate, nasal irritation, runny nose, tears (following nasal admin); uterine bleeding, violent contractions, increased tone of uterus and spasm, nausea, vomiting.
Heart- Premature ventricular contractions, hypertensive episodes.
Gastrointestinal- Nausea and vomiting.
Metabolic-Nutritional- Water intoxication with convulsion, coma, and death.
Miscellaneous- Severe allergic reactions, absence of fibrinogen in the plasma that could be fatal, blood clot in pelvic region.
What are the other precautions for Oxytocin?
Risk of water intoxication when used at high doses for prolonged periods.What are the storage conditions for Oxytocin?
Intravenous: Store at 2-8 °C. Nasal: Store at 2-8 °C. It is usually handled and stored by a health care provider.Schedule : H
Prescription drugs - Drugs to be sold only under the prescription of a Registered Medical Practitioner.