- Screening and Surveillance for the Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer and Adenomatous Polyps, 2008: A Joint Guideline from the American Cancer Society, the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, and the American College of Radiology. CA Cancer J Clin 2008;58;130-160.
What is Colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy is a widely used endoscopic technique used to screen individuals for colorectal cancer. It is very sensitive in detecting colorectal cancers.
Colonoscopy is a widely used screening test for colorectal cancer. A number of other tests are also available; the details of these could be accessed at the link below:
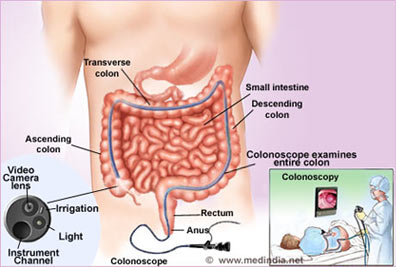
Colonoscopy is an endoscopic procedure in which a thin tube with a camera at the tip is introduced through the anus till the start of the colon. It permits direct examination of the entire colon and detects abnormalities like polyps or cancers.
Prior to colonoscopy, the patient has to undergo bowel preparation. This is done to ensure that the inner lining of the colon is clearly visible to the examiner. The person has to follow some diet restrictions along with laxatives and enemas for bowel preparation. Bowel preparation is not always acceptable to all people and may deter some individuals from undergoing colonoscopy.
The individual is sedated just before undergoing colonoscopy. The doctor first examines the anus by introducing a gloved finger, the examination being referred to as digital rectal examination. He them introduces the lubricated tip of the colonoscope through the anus and rectum up to the start of the colon. Air is also insufflated for better visualization. The inner lining of the colon is examined as the colonoscope is withdrawn out. Polyps if observed may be removed during this procedure. Biopsies of suspicious lesions can also be taken.
Colonoscopy should be repeated at least every 10 years.
1. Who should undergo colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy is one of the preferred tests used in screening for colorectal cancer. Individuals over the age of 50 years at average risk for developing colorectal cancer should undergo colonoscopy or any of the other screening tests on a regular basis.
2. How often should colonoscopy be repeated?
If all findings are normal, colonoscopy may be repeated every 10 years. People at high risk for developing colorectal cancer may have to start undergoing the test at an earlier age and repeat it more often. These include:
- Individuals previously diagnosed with adenomatous polyps
- Individuals who have earlier undergone surgery to remove colorectal cancer
- Individuals with immediate relatives diagnosed with precancerous colorectal polyps or colorectal cancer
- Individuals with inflammatory bowel disease like Crohn’s disease
- Individuals suffering from one out of two specific syndromes i.e. hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC) or familial adenomatous polyposis
3. Who should not undergo colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy should not be done in any person if the risks of the procedure are likely to outweigh the benefits. It is best avoided during pregnancy.
4. What are the advantages of colonoscopy?
The advantages of colonoscopy are:
- Colonoscopy permits direct visualization of the entire lining of the colon. Thus it is a very sensitive method for detecting colorectal cancer
- Biopsy of any abnormality observed during the procedure can be taken
- If the suspicious lesion is small, it can be completely removed in the same sitting. Thus, during the screening procedure, treatment of certain lesions is also possible
- Any other condition affecting the bowel can also be diagnosed during the same procedure
- If any of the other colorectal screening tests detects an abnormality, it should be followed by a colonoscopy. Thus, doing colonoscopy as the first choice avoids a repeat procedure in case of any abnormality
5. What are the disadvantages of colonoscopy?
The disadvantages of colonoscopy are:
- Some people find bowel preparation too tedious and may not be willing to undergo the procedure
- Sedation is required for colonoscopy. Though this could be a disadvantage, some people may prefer a procedure with sedation to avoid discomfort
- Abdominal cramps and bloating may occur following the procedure, especially if air is used for visualization. This complication can be reduced by using carbon dioxide instead of air
- Bleeding may occur following the procedure, especially if the patient has undergone removal of polyp or biopsy of suspicious lesion
- Examination may be incomplete in case of incomplete bowel preparation or conditions where it may be difficult to advance the colonoscope through the entire bowel
- Complications due to sedation used during the procedure include low blood pressure and cardiac arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms)
- Perforation of the bowel is a rare but serious complication of colonoscopy
- Rupture of the spleen and small bowel obstruction could occur, which are again extremely rare
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which doctor should I visit to get a colonoscopy done?
You should visit a gastroenterologist to get a colonoscopy done. The success of the procedure, that is, the chances of detecting a cancerous lesion, depends on the skill of the examiner; hence it would be better to get the test done by an expert with adequate experience in the field.
2. What is the difference between flexible sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy?
Flexible sigmoidoscopy is a faster procedure compared to colonoscopy. It does not require sedation and the person can return to work soon after the procedure. In contrast, colonoscopy takes longer time and requires sedation. Some people may prefer to be sedated, thus this could be an advantage in such patients. Colonoscopy permits examination of the entire colon whereas in sigmoidoscopy, only the lower portion of the colon is examined. Thus a number of cancers especially those on the right side could be missed in flexible sigmoidoscopy. Flexible sigmoidoscopy should be repeated every 5 years whereas colonoscopy every 10 years.