Treatment
Acoustic neuroma treatment is usually multi disciplinary and the team of doctors will include a neurologist, a neurosurgeon, an oncologist (despite the tumor being benign) a radiologist, a specialist nurse, a dietician , a physiotherapist and other health specialists.
The number of factors such as general health, size and position of the tumour will help to decide on the type of treatment that would be offered to the patient. The benefits of these treatments will, again, depend on several factors and will vary with individuals.
If the tumor is small with very little symptoms, it may not need any radical treatment. One fourth of all acoustic neuromas are managed through regular monitoring (with the help of imaging studies) and by using hearing aids when deemed necessary.
However the indicated treatments for acoustic neuromas are Microsurgery and radiotherapy.
Acoustic neuroma may be completely removed with the help of microsurgery after which further treatment becomes redundant. On several occasions the neurosurgeon leaves behind a small part of the tumor, during surgery, to avoid nerve damage.
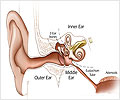
However, loss of hearing may be unavoidable as a surgical side effect. This situation can be salvaged to a large extent by fitting a hearing aid that helps to divert sounds from the affected ear to its healthier counterpart.
Sometimes, during surgery, the facial nerve may be damaged leading to temporary, or permanent numbness or drooping (also called palsy) of one side of the face. This condition can impair facial movements, such as chewing or blinking. Massage and physical exercises carried out under the supervision of experts can usher in relief.
Radiotherapy, which uses high-energy rays to kill tumor cells is an alternative treatment for acoustic tumors. It is mainly done by two methods gamma knife radiosurgery and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy. These techniques do not completely remove the tumor but is less likely, than surgery, to cause hearing loss. It can be given as a single dose or given over different sessions.
Many surgeons feel that the neuromas are more difficult to be removed surgically after radiation treatment.
There are risks associated with radiation too -
- The neuroma may change from benign to malignant
- It can cause the formation of secondary tumors(eg is glioblastoma)
- In the irradiated tissue surrounding the site of the tumor These risks are more likely to occur in patients already suffering from neurofibromatosis type II.
Due to these reasons patient who is being treated by radiation requires a life time of monitoring through MRI scans.