- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS): Questions and Answers about Sprains and Strains. Waterman BR, Owens BD, Davey S, Zacchilli MA, Belmont PJ Jr. The epidemiology of ankle sprains in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010 Oct 6;92(13):2279-84: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: Repetitive Motion Disorders
About
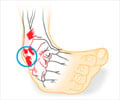
The region where the foot and the leg meet is called ankle; the scientific term for ankle is talocrural region. The ankle region comprises of three bones: the talus (in the foot), and the tibia and fibula (in the leg). Three joints are included in the region.
The ankle has to support the entire weight of the body, and is thus extremely vulnerable to injury. Millions of people get treatment for ankle related problems such as sprains, strains and fractures every year. It would be apt to say that the ankle is among the most commonly injured parts of the body.
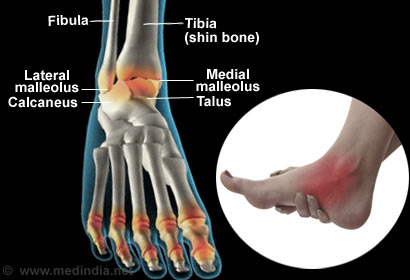
Common Causes of Ankle Pain
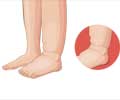
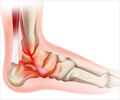
Ankle Sprain: A sprain results from the overstretching of ligaments of the ankle joint. The ligament may get torn completely or partially. The severity of sprain is decided by the degree of ligament tear. Ankle sprain occurs commonly during sports events that involve running, jumping, or walking. Movements of the sprained joint cause pain.
Achilles Tendonitis: Overuse of the Achilles tendon (a tendon of the posterior leg) results in little tears that cause pain and discomfort. The Achilles tendon, the largest tendon in our body, connects the calf muscles of leg to the heel bone. It is active especially during walking, running and jumping.
Stress Fracture: When a bone is repeatedly subjected to forces, it may develop cracks. This type of overuse injury is called stress fracture. Normally muscles absorb some amount of shock thereby reducing the stress on bones. But a fatigued muscle (during overuse) transfers the stress to the bone leading to stress fractures. When direct pressure is applied at the affected bone, pain is felt.
Arthritis: Inflammation of joints can cause significant discomfort and pain. Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease, is the commonest form of arthritis. Arthritis can also be due to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
Management of Ankle disorders
Rehabilitation of the ankle is the cornerstone of managing ankle related disorders. This involves a stepwise manner of exercises that target strengthening and stretching the ankle after injury. It should be understood that an ankle injury increases the risk of a re-injury to about 40 to 70%. Exercises range from non-weight bearing exercises, resisted exercises, to weight bearing activities.
Fractures require the help of an Orthopedician (bone specialist). Arthritis requires a teamed approach that involves various specialities like Internal Medicine, Orthopaedics, Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How is a sprain different from strain?
Sprain is due to a stretch or tear of a ligament. Ligament is what connects bones at a joint. In strain, either a muscle or tendon is injured. Sprain most commonly occurs at the ankle. Strains are common in the back and the hamstring muscle (hamstring is actually a group of tendons formed by posterior thigh muscles).
2. What are the signs and symptoms of sprain?
Pain, swelling, bruising, difficulty with movement are the common symptoms of sprain. The severity depends on the degree of ligament involvement.
3. How can sprains and strains be treated?
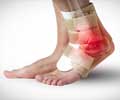
Give adequate Rest to the affected part. Application of Ice packs (for not than 20 minutes in a single setting) helps. Compression bandages, casts, or splints can be used to ease swelling. Swelling can also be reduced by keeping the ankle Elevated. Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation (‘RICE’ therapy) are advised during the first 24 to 48 hours after injury.
4. Can sprains and strains be prevented?
It is not possible to absolutely prevent an incidence of sprain or strain! Since we can’t exactly predict when either will occur. Maintain a healthy weight; maintain adequate nutrition so as to have healthy bones and muscles. Don’t avoid warm up exercises and stretches before participating in sports or exercise workouts. Wear shoes that fit well. Avoid exercises or sports when you are tired or have pain.
5. What are Repetitive Motion Disorders?
Repeated activities that we perform in the course of our normal life or work lead to a family of muscular conditions called Repetitive Motion Disorders (RMDs). Carpal tunnel syndrome that arises following repeated and strenuous work with a keyboard, repeated forceful use of a digit leading to trigger finger are different examples of RMDs.