- Harrison's Textbook of Medicine Cecil's Textbook of Medicine - (https://www.who.int/)
About
Asbestosis is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that occurs due to long- term exposure to asbestos fibres.
Asbestosis particularly affects the parenchymatous tissues of the lungs and has gained increased significance due to its link to
Asbestos is a group of minerals, comprised of long, thin and fibrous crystals. It gained widespread usage during the industrial revolution. It is ideally suitable for insulation, due to its ability to withstand heat, and is resistant to destruction by several physical and chemical agents.
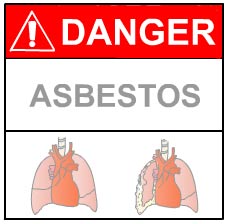
Asbestos fibres are of varying lengths and sizes. There are two major types of asbestos namely chrysotile, or the serpentine type and the amphiboles or the straight type. Chrysotile is the more dangerous of the two varieties. All types of asbestos are capable of causing fibrosis (shriveling) of the lung tissue.
Asbestosis, as a medical problem, was recognized early in the 20th century. A few decades later studies established
Developing countries still face the problem of widespread usage of this material by a variety of industries, such as textiles, insulators, fire-proofing, reinforcement of cement and brake linings.
Miners are at a greater risk of exposure to asbestos. Construction workers too are at a higher risk of exposure, as asbestos is frequently used in construction industries. The risk level for the occupants of such buildings is, however, quite negligible.
A relatively rare disease, asbestosis, mostly occurs in people who are constantly exposed to asbestos fibres. Those who are at the worst risk include people who directly come in contact with asbestos material at their work place.
Exposure to asbestos fibers invokes an immune response in the exposed individual. When this exposure is long-term, it leads to fibrosis of the lung, a typical feature of asbestosis. Shortness of breath is usually the presenting symptom.
Asbestosis may be diagnosed by ruling out other diseases with similar symptoms. Pulomonary Function Tests, chest X-rays and CT scans are some of the diagnostic tests usually employed. In some cases, a biopsy of the lung may be called for.
Asbestosis is bereft of a specific treatment regime. Respiratory infections are controlled with the help of antibiotics. Management of the disease, through lifestyle changes is, often, the only choice. More care must be taken to prevent the disease, especially by the high - risk group.