- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine 17th edition
- Brunberg JA. Ataxia. American Journal of Neuroradiology 2008; 29:1420-1422
About
Ataxia affects coordination. Gait becomes unstable and the patient loses balance. The cerebellum or its inputs and/or outputs are affected. The causes are mostly related to our nervous system.
Ataxia is a condition where a person lacks coordination during voluntary movement. He walks with an unstable gait and loses balance. His trunk may sway from side-to-side. He may show symptoms like slurring of speech, involuntary eye movements, difficulty with swallowing and tremor with movement. MRI scans helps in its diagnosis and the treatment of the conditions depends on its cause.
Anatomy and Physiology
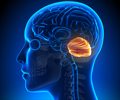
The cerebellum is a part of the brain that is located in the lower back portion of the skull. It helps a person to maintain balance and posture. It is also the centre for coordinating voluntary movements. It receives signals from sense organs that include inner ear, eye, muscle, joints and skin. These signals travel through the spinal cord to the cerebellum. The cerebellum also receives inputs and sends output to other parts of the brain such as brainstem, thalamus, vestibular nuclei and cortex.
Any condition that affects the cerebellum or signals going to and from the cerebellum causes ataxia.
- When the cerebellum is mainly affected, the ataxia is called cerebellar ataxia.
- If the cerebellum is unaffected but is unable to receive signals, the ataxia is called sensory ataxia.
In sensory ataxia, the spinal cord, thalamus, cortex or nerves may be affected. It can be differentiated from
In vestibular ataxia, the signals from the inner ear are unable to reach the brainstem and cerebellum. A patient with vestibular ataxia often experiences vertigo i.e. a feeling that either the patient or his surroundings are spinning. In addition, he may exhibit involuntary movement of the eyes and loss of balance. Some common causes include inflammation of the inner ear or vestibular nerve that carries signals, trauma, lack of blood supply and some drugs that affect the inner ear.
Ataxia is usually diagnosed with MRI and genetic studies are done in cases of hereditary ataxias. They do not have any specific treatment. Some cases may recover spontaneously whereas others may undergo further complications.