Diagnosis of Biliary Cirrhosis
The presence of antimitochondrial autoantibodies (AMA) and increase in enzymes like alkaline phosphatase help to diagnose primary biliary cirrhosis.
The following tests are used to diagnose biliary cirrhosis:
- Blood tests: Blood tests show the presence of anti-mitochondrial autoantibodies (AMA). This test is very important in the diagnosis of PBC. The blood level of liver enzymes alkaline phosphatase and gamma glutamyl transferase is increased. The level of other liver enzymes and cholesterol may also be high. The number of red and white blood cells and platelets may be low. Blood tests to measure thyroid function should also be carried out due to the association of PBC with thyroid disease.
- Ultrasound / CT scan / MRI: Imaging studies like ultrasound, CT scan and MRI help the physician check for abnormalities in the liver and bile ducts.
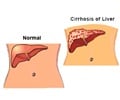
- Biopsy: Biopsy of the liver helps to diagnose the condition, though it is not always necessary.
- Bone density testing: Bone density testing may be done to rule out thinning of bone due to PBC.