| Infection | Causative Microorganism | Clinical features | Prevention |
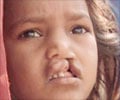
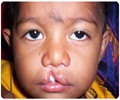
| Rubella / German Measles | Virus, potent teratogen | Risk of infection during the first trimester is 20%. Leads to congenital Rubella Syndrome- Cataract, cardiac defects, and deafness. Less commonly - Chorioretinitis, glaucoma, microphthalmia (Small, abnormal eyes), and tooth defects. | Rubella vaccine is usually administered to girls aged 10-14 years. It is recommended for women of child-bearing age who are found to be seronegative, Seronegative pregnant women should be vaccinated in the early postpartum period. Pregnancy should be avoided for at least one moth after vaccination. |
| Cytomegalovirus infection | Virus, cytomegalovirus (CMV) | Most common viral infection the human fetuses. Spontaneous abortion in first trimester, intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), microphthalmia, chorioretinitis, blindness, microcephaly (very small head), mental retardation, cerebral palsy, hepatosplenomegaly (enlargement of the liver and spleen). | Practice good personal hygiene; handwashing with soap and water is effective. Care should be taken while handling children and diapers. |
| Herpes Simplex infection | Herpes Simplex virus (HSV). Infection commonly occurs during delivery. | Spontaneous abortion, premature delivery, skin related defects, microcephaly, microphthalmia, spasticity, retinal dysplasia (detachment of the retina), and mental retardation. | Avoiding contact with someone who has an active herpes infection can prevent the disease during pregnancy. Aseptic precautions during delivery are necessary. |
| Chicken Pox | Varicella zoster virus | Scarring of fetal skin, muscular atrophy (reduction in muscle size), rudimentary digits/ fingers and mental retardation. | Chicken Pox vaccine |
| HIV infection | Human Immuno Deficiency Virus | Growth failure, Craniofacial defects (defects of the face and head). | General preventive measures for HIV also hold good during pregnancy. Do not share injections, needles or syringes with anybody else. Do not breast feed your baby if you have an HIV infection. Talk to your doctor regarding the options available if you are already infected with HIV. |
| Toxoplasmosis | Toxoplasma gondii, eating raw or poorly cooked meat (pork/lamb). | Changes in the brain and eyes, microcephaly, microphthalmia, hydrocephaly (excessive fluid/ CSF accumulation in the brain). | Avoiding contact with pet animals (cat, dog, rabbit) and eating safe, properly cooked meat. |
| Syphilis | Treponema pallidum can be infected at any stage of pregnancy. | Primary infection: Congenital deafness, abnormal teeth, bones, hydrocephalus, mental retardation. Secondary infection: Destructive lesions of the palate and nasal septum, dental abnormalities (Hutchinson’s teeth), abnormal facial features. | |
| Viral Infection | Human parvovirus B19 | Eye defects, degenerative changes in fetal tissues. | No vaccination available. Practice of safe hygienic habits can reduce the risk. |
| Encephalitis | Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus | Microcephaly, microphthalmia, cerebral agenesis, CNS necrosis, hydrocephalus. |