- Bradycardia - (https://www.cedars-sinai.edu/patients/health-conditions/bradycardia.aspx)
- Bradycardia: Slow Heart Rate - (https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/arrhythmia/about-arrhythmia/bradycardia--slow-heart-rate)
- Signs and Symptoms of Bradycardia - (https://www.cardiosmart.org/heart-conditions/bradycardia/understand-your-condition/signs-and-symptoms)
- Diagnosing Bradycardia - (https://www.virginiamason.org/bradycardia)
- Treatment of Bradycardia - (https://www.health.harvard.edu/a_to_z/bradycardia-a-to-z)
About
Abnormal rhythms of the heart can adversely affect the pumping ability of the heart. A heart rate of more than 100/min is called tachycardia and a rate of less than 60/min is called bradycardia, or a slow heart rate.
Causes of bradycardia may be physiological as seen during sleep and in athletes. When the bradycardia is pathological it results from a failure of impulse initiation or impulse conduction. This is due to the Sino Atrial (SA) Node Dysfunction or due to AtrioVentricular (AV) block.
The patient may not have any symptoms at all; some present with a wide range of symptoms. Electrocardiographic recordings during an attack are most helpful in diagnosis. The treatment is tailored according to the symptoms by the cardiologist.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Bradycardia: Slow Heart Rate
Go to source)
Causes of Bradycardia
Bradycardia can be physiological or pathological
Physiological Causes
a) Athletes
An athlete’s heart is considerably large and strong and this allows him to pump a large stroke volume output per beat even during rest. During periods of rest, the large volumes of blood pumped into the arterial tree with each beat initiates feedback circulatory reflexes to cause bradycardia.

b) During Sleep
Pathological Causes
Bradycardia results from a failure of impulse initiation or impulse conduction.
Thus bradycardia can be caused by
- Reduced Automaticity as in Sinus bradycardia
- Blocked or automatically slow conduction as in atrioventricular blocks
The most common causes of pathologic bradycardia are
SA NODE DYSFUNCTION: SA (sinoatrial) node is a specialised bundle of neurons that generate electrical impulses in the heart, it is called the pacemaker.
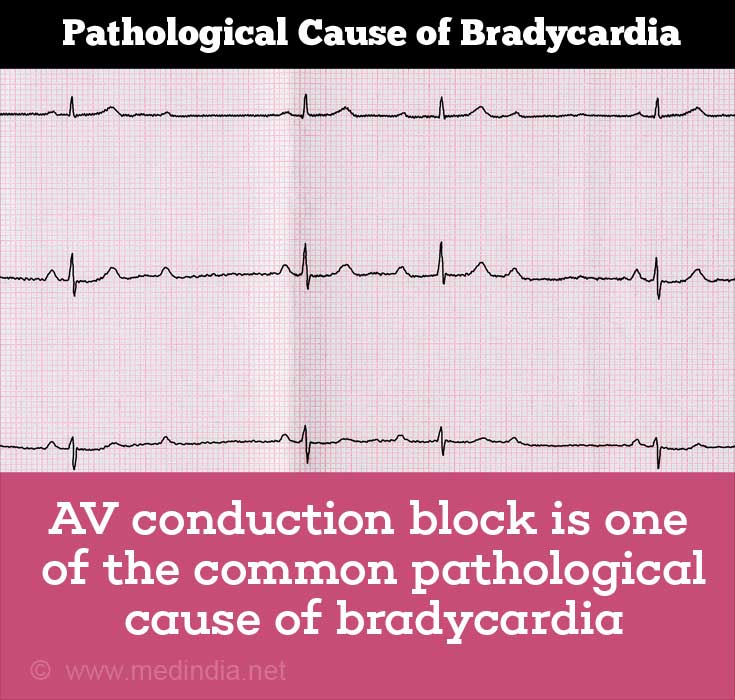
AV CONDUCTION BLOCK: The AV (atrioventricular) node is a small mass of specialized cardiac muscle fibres that receive impulses from the SA node.
SA Node Disease
Causes are Intrinsic and Extrinsic
Extrinsic Causes
Extrinsic is reversible and due to
1. Autonomic causes
- Carotid sinus hypersensitivity
- Vasovagal Stimulation
- Sometimes even a mild external pressure on the neck elicits a strong baroreceptor reflex, causing extreme bradycardia due to vagal-acetyl choline effects on the heart. This happens in carotid sinus syndrome where the pressure receptors (baroreceptors) in the carotid sinus region of the carotid artery walls are very sensitive.
2. Drugs like β blockers, Calcium channel blockers, Digoxin, and others
3. Hypothyroidism
4. Sleep Apnea
5. Endotracheal suctioning
6. Hypothermia
7. Increased intracranial pressure
Intrinsic Causes

2. Sinus node disease ( Sick Sinus Syndrome)
4. Cholestatic jaundice
5. Idiopathic fibrotic disease.
7. Amyloidosis
8. Chest Trauma
9. Radiation Therapy
10. Post Surgical
Rare Heritable Form of Sinus Node Disease:
Atrioventricular Conduction Disease
This can cause pathologic bradycardia and the causes for Atrioventricular block are-
1. Carotid sinus hypersensitivity
2. Vasovagal
3. Hyperkalemia
5. Drugs like β blockers, Calcium channel blockers, Digitalis and others
6. Infections like Endocarditis, Tuberculosis and others
8. Amyloidosis
9. Tumors like lymphomas, melanomas and others
10. Coronary artery disease
11. Congenital heart disease and other congenital, heritable conditions(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Bradycardia
Go to source)
Symptoms of Bradycardia
SA node dysfunction may be completely asymptomatic or the patient may present with syncopal attacks, palpitations or fatigue.
It could also be associated with tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome where symptoms may be due to slow and fast heart rates.
In many cases symptoms can result from concomitant cardiac disease.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Signs and Symptoms of Bradycardia
Go to source)
Diagnosis of Bradycardia
SA node dysfunction is a clinical or an electrocardiographic diagnosis.
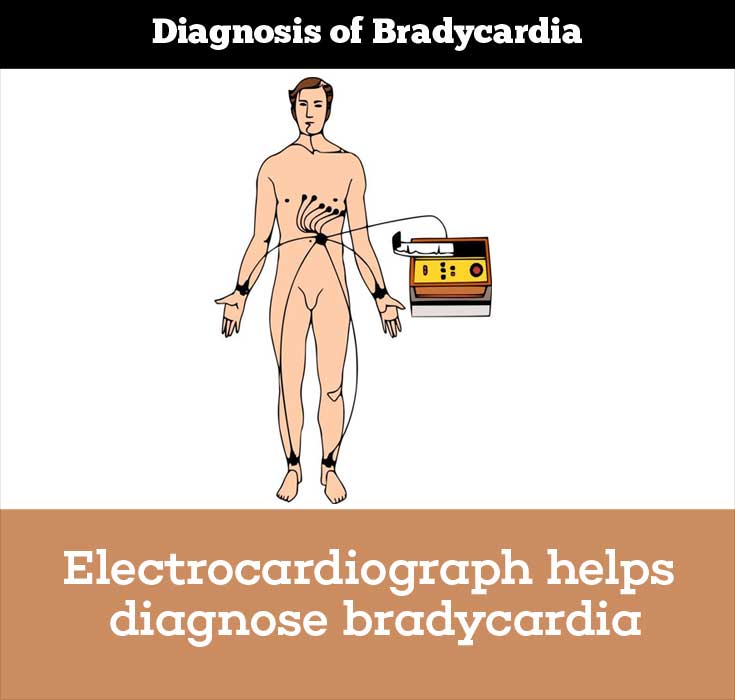
Longer term recording Holter or event monitors may permit correlation of the symptoms with cardiac rhythm.
Autonomic nervous system testing is useful in diagnosing carotid sinus hypersensitivity.
Documentation of the sinus pauses during an attack of symptoms provides the best diagnostic information.(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diagnosing Bradycardia
Go to source)
Management of Bradycardia
In certain circumstances, sinus bradycardia requires no specific treatment or only temporary rate support.
Pacemaker implantation is the primary therapeutic intervention in patients with symptomatic SA node dysfunction and in patients with atrioventricular dysfunction.

Chronic pharmacologic therapy for sinus bradyarrhythmias is limited.(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Treatment of Bradycardia
Go to source)