- Hemorrhagic Stroke - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559173/)
- What Is the Difference Between Ischemic stroke and Hemorrhagic Stroke? - (https://www.pacificneuroscienceinstitute.org/blog/stroke/what-is-the-difference-between-hemorrhagic-and-ischemic-stroke/)
- Strokes and Haemorrhages (bleeds) - (https://headway.ie/about-brain-injury/types-of-brain-injury/strokes-and-haemorrhages/)
About
When it comes to neurological emergencies, two terms often heard are "brain hemorrhage" and "stroke." While they share similarities, understanding the differences between them is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
What is Brain Stroke and Brain Hemorrhage?
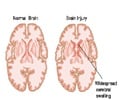
A stroke occurs when there is a disruption in the blood supply to the brain, leading to cell death and brain damage. There are two main types of strokes: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes result from a blockage in a blood vessel supplying the brain, while
Did You Know?
Brain hemorrhage, though less common, is deadlier than ischemic stroke.Brain Hemorrhage
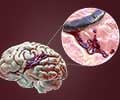
Brain hemorrhage, or intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), is a specific type of hemorrhagic stroke characterized by bleeding inside the skull and brain. This bleeding can occur due to various factors such as hypertension, aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, or trauma. It is a severe medical emergency that requires immediate attention as it can lead to brain damage, neurological deficits, and even death(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Go to source).
Brain Stroke
On the other hand, ischemic strokes occur when a blood clot obstructs blood flow to a part of the brain. These clots can originate from other parts of the body and travel to the brain (embolic stroke) or form directly in the brain's blood vessels (thrombotic stroke). Ischemic strokes are more common than hemorrhagic strokes and also require urgent medical intervention to minimize brain damage and prevent complications.
Difference Between Brain Hemorrhage and Stroke
|
Feature |
Brain Hemorrhage |
Stroke |
|
Definition |
Bleeding inside the skull and brain tissue. |
Disruption of blood flow to the brain, causing cell death. |
|
Types |
Intracerebral hemorrhage (within brain tissue) |
Ischemic (blockage) and Hemorrhagic (bleeding) |
|
Causes |
Hypertension, aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, trauma. |
Blood clots, embolisms, atherosclerosis. |
|
Symptoms |
Sudden severe headache, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, neurological deficits. |
Sudden weakness/numbness, difficulty speaking/understanding, severe headache, dizziness, loss of balance/coordination. |
|
Diagnosis |
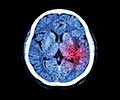
CT scan, MRI, neurological assessment. |
CT scan, MRI, physical examination, neurological assessment. |
|
Treatment |
Medications to control blood pressure, surgery to remove clots, repair damaged blood vessels. |
Clot-busting medications, mechanical interventions (thrombectomy), blood thinners (for certain types). |
|
Prognosis |
Prognosis can be severe, depending on the extent of bleeding and location in the brain. |
Prognosis varies depending on the severity and timing of treatment. |
|
Mortality Rate |
Higher mortality rate compared to ischemic strokes. |
Mortality rate depends on the type and severity of stroke. |
|
Complications |
Brain damage, neurological deficits, increased intracranial pressure, coma. |
Brain damage, paralysis, speech impairments, cognitive deficits. |
|
Timeframe for Treatment |
Immediate medical attention required to minimize brain damage. |
Immediate medical attention crucial to restore blood flow and prevent lasting damage. |
One significant difference between brain hemorrhage and stroke lies in their underlying causes and treatment approaches(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
What Is the Difference Between Ischemic stroke and Hemorrhagic Stroke?
Go to source).
While ischemic strokes often involve the administration of clot-busting medications or mechanical interventions to restore blood flow, hemorrhagic strokes require measures to control bleeding and reduce pressure on the brain. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the clotor repair the damaged blood vessel.
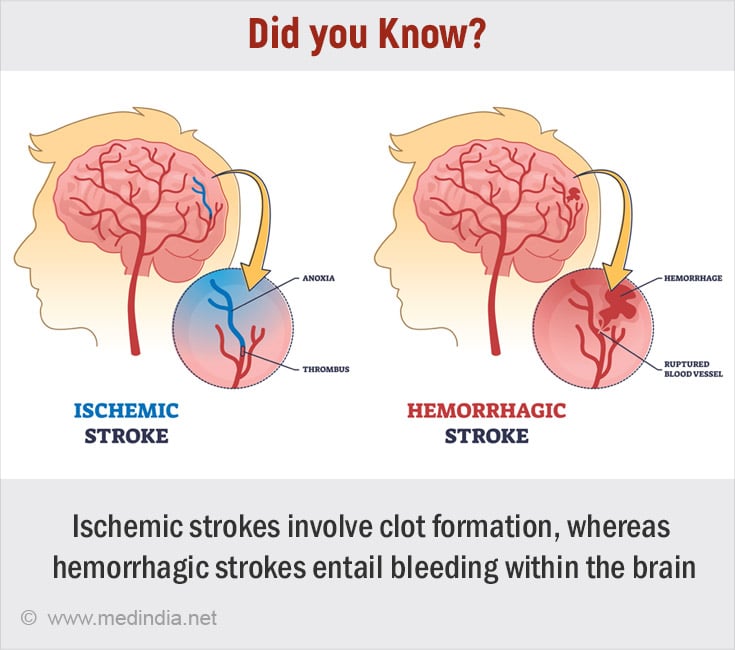
The symptoms of brain hemorrhage and stroke can overlap, including sudden weakness or numbness, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, severe headache, dizziness, and loss of balance or coordination. However, the sudden onset of a severe headache is more characteristic of a hemorrhagic stroke, particularly if it is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, or loss of consciousness(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Strokes and Haemorrhages (bleeds)
Go to source).
Summary
In summary, while brain hemorrhage and stroke are both neurological emergencies that require immediate medical attention, they differ in their underlying causes, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. Understanding these differences can help individuals recognize the signs and symptoms promptly, leading to timely interventions and improved outcomes. If you suspect you or someone else is experiencing symptoms of a stroke or brain hemorrhage, seek emergency medical care without delay.