Glossary
Anemia: A condition in which a decreased number of red blood cells may cause symptoms including tiredness, shortness of breath, and weakness.Benign growth: A swelling or growth that is not cancerous and does not spread from one part of the body to another.
Biopsy: The surgical removal of tissue for microscopic examination to aid in diagnosis.
Cancer: A group of diseases in which malignant cells grow out of control and spread to other parts of the body.
CAT scan (CT scan): A test using computers and X-rays to create images of various parts of the body
Chemotherapy: The treatment of cancer with drugs
Comorbid: A separate condition that exists or has been present in addition to the main disease under treatment, which affects the patient.
Cognitive: Pertaining to the mental process of thought, including perception, reasoning, intuition, and memory
Edema: The accumulation of fluid in part of the body.
Fine-needle aspirate: A procedure in which a needle is inserted, under local anesthesia, to obtain a sample for the evaluation of suspicious tissue
Immunotherapy: The artificial stimulation of the body's immune system to treat or fight disease.
Lesion: A lump or abscess that may be caused by injury or disease, such as cancer.
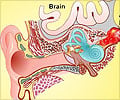
Lymph nodes: Hundreds of small oval bodies that contain lymph. Lymph nodes act as our first line of defense against infections and cancer.
Malignant tumor: A tumor made up of cancer cells of the type that can spread to other parts of the body.
MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging): A sophisticated test that provides in-depth images of organs and structures in the body.
Myelogram: An x-ray procedure by which a dye is injected into the spinal column to show any pathology of the spinal cord.
Oncologist: A doctor who specializes in oncology.
Oncology: The study and treatment of cancer. Doctors who specialize in oncology are called oncologists.
Primary tumor: The original cancer site. For example, breast cancer that has spread to the bone is still called breast cancer.
Radiation therapy: X-ray treatment that damages or kills cancer cells.
Radiologist: A doctor who specializes in the use of X-rays to diagnose and treat disease
Risk factor: Anything that increases a person's chances of developing cancer, for example, smoking and lung cancer.
Side effects: Secondary effects of drugs used for disease treatment.
Steroids: A type of hormone.
Tumor: An abnormal overgrowth of cells. Tumors can be either benign or malignant.
X-ray: High-energy electromagnetic radiation that are used to diagnose and treat disease.
Glial cells: Also called glia or neuroglia, they are the non-neuronal cells in the brain and spinal cord. They are vital to homeostasis, form an insulating covering of nerves, and provide support and protection for neurons.