Glossary
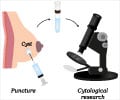
Prophylactic Mastectomy - preventive removal of breasts.FNAC - Fine needle Aspiration cytology - a very fine needle is used to puncture a swelling and the cells are looked under microscope to see if are of cancerous nature. Usually no local anesthesia is required.
PCR or Polymerase Chain Reaction. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a common, indispensinble molecular biology technique that has automated the multiplication of gene sequence. PCR helps researchers to produce millions of copies of a specific DNA sequence in less than two hours and has multiple applications. It was first developed by Kary Mullis in 1984. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on PCR in 1993. Some of its application today includes - DNA cloning for sequencing, in the diagnosis of hereditary diseases; for forensic identifying of genetic fingerprints, for paternity testing and in detection and diagnosis of infectious diseases.
BRCA(breast cancer) gene - It is a gene located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 17 at band 21 and its mutations is associated with a significant increase in the risk of breast cancer, as well as ovarian cancers. It is a 'tumor suppresor gene' which means it is protective in nature and helps in DNA repair.
HER1 & HER2 - stands for "Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor1 or Receptor2 " are proteins that are present on the surface of the cells of breast cancer and makes the cancer more aggresive.
Salpingo-oophorectomy - Removal of fallopian tube along with ovaries.