- What is Cauliflower Ear? - (http://www.ohniww.org/cauliflower-ear/)
- Summers A. Managing auricular haematoma to prevent ''cauliflower ear''. Emerg Nurse. 2012 Sep;20(5):28-30. Review. PubMed PMID: 23256352.
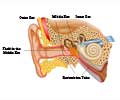
What is Cauliflower Ear?
Cauliflower ear is actually a colloquial term used to describe the appearance of the ear following auricular hematoma. An auricular hematoma is a condition in which there is swelling and reddening of the outer ear because of accumulation of blood between the cartilage and the tissue surrounding it (called perichondrium). This occurs on account of trauma to the ear, which is why you may also notice some amount of bleeding and external injury at the same time. Auricular hematoma, if neglected, results in deformities of the outer ear; the deformed ear is called cauliflower ear.
The terms auricular hematoma and cauliflower ear are used interchangeably in popular media, which is why people simply refer to the condition as cauliflower ear.
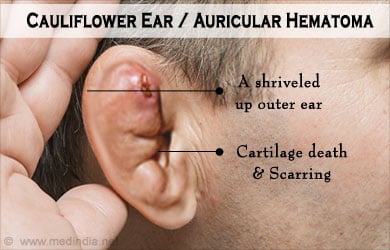
If an auricular hematoma is not treated promptly, it can result in permanent damage to the ear cartilage and, scarring and disfigurement are permanent. When the condition is allowed to progress this far, it is a lot harder to treat and the damage will very often be irreversible. The most effective way to deal with this problem is by attending to it immediately and by preventing any disfiguration in the first place.
As bizarre as it may sound, the lumpy disfigured appearance of the ear associated with cauliflower disease is proudly worn as a badge of honor among some sportsmen and athletes! This is because of its association with rough contact sports like boxing, wrestling, martial arts and rugby, as the condition itself results from blunt force trauma. Sporting cauliflower ears is in some ways viewed as earning your stripes. Nevertheless sportsmen and athletes today are more aware of the risks of injury and prefer to avoid such unnecessary risks.
What are the Causes of Cauliflower Ear?
The outer ear is mainly comprised of cartilage that lends the ear its distinctive contours. It also gives it some amount of flexibility and movement. As blood vessels do not supply blood to the cartilage, the cartilage must receive necessary nutrients from the surrounding tissue called the perichondrium. “Blunt force trauma” to the ear can result in accumulation of blood between the cartilage and the perichondrium, disturbing blood flow to the cartilage and resulting in localized swelling. The presence of a hematoma may stimulate the growth and formation of new cartilage and fibrous tissue, but the new cartilage is often asymmetric. This is the reason for the deformity or cauliflower ear.
Auricular hematomas may also develop on account of repeated and frequent friction during wrestling when the ears may be compressed or pressed against the floor or mat. In this case as well, the perichondrium may be separated from the cartilage causing bleeding between them.

What are the Symptoms and Signs of Cauliflower Ear?
The symptoms of cauliflower ear, or more importantly auricular hematoma, are not hard to recognize, but they may vary slightly depending on severity of the trauma that the ear is subjected to. Some of the common symptoms include:
- Swelling and bruising of the ear
- Ear pain that may be mild to severe
- Abnormality or changes in the normal curvature of the ear
- Facial swelling
In severe cases, the facial trauma may also cause other accompanying symptoms like:
- Hearing loss
- Tinnitus
- Bleeding from the ear
- Headaches

Medical help should be sought as soon as possible, especially if the trauma is severe. The symptoms will usually subside as scarring and disfigurement occurs, but by this time cauliflower ear develops and it may be too late to seek treatment.
How is Cauliflower Ear Diagnosed?
Auricular hematoma is almost always diagnosed through physical examination and patient history as it is fairly easy to recognize. There will almost always be swelling and the ear will appear misshapen. If there is any uncertainty about the diagnosis, your doctor will probably withdraw some of the fluid from the swollen area with a needle to establish if it is filled with blood or pus due to abscess formation.
Make it a point to inform your doctor of all the symptoms you have experienced and any other medical conditions that you suffer from or are receiving treatment for. In addition to standard tests and physical examination, doctors may also recommend imaging tests like x-rays or CT scans to rule out any facial and skull base injuries.
How do you Treat Cauliflower Ear?
Cauliflower ear can be easily prevented if treatment is provided as soon as the symptoms of auricular hematoma start to surface. The greater the delay in treatment, the more difficult it becomes to manage the problem. This is because if there is no intervention, blood supply to the cartilage can be greatly reduced, increasing the risk of cauliflower ear deformity.
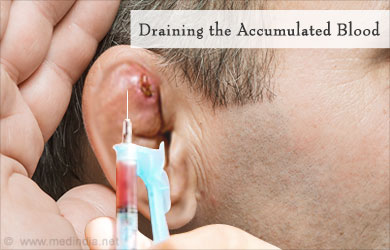
The first step of treatment is to drain the blood that is trapped and to provide treatment in case of any infection. The hematoma is drained via an incision that is made in the ear. Smaller hematomas can be aspirated with a needle in very early stages. Anti-inflammatory medications are also prescribed to reduce inflammation. Compressive dressing is usually applied to compress the wound. If this is done promptly, there is little to no chance of any deformity developing. Doctors often prescribe antibiotics to minimize the risk of infection as this would greatly complicate the problem.
Depending on the severity of the trauma responsible for your condition, there may even be a need for stitches to reconnect the tissues. The compressive or pressure dressing that is used will generally need to remain for a few days or a week at least. Make sure that you follow the advice of your doctor and go back for regular checks as needed. This is extremely important as the ear will need to be monitored in case of any infection or if a change in treatment is required.
In cases with a worsening superimposed infection, the patient may actually need to be admitted so that intravenous antibiotics can be administered. Exploration and washout under general anesthesia may also be necessary.
Prevention of Cauliflower Ear
It is much easier to prevent cauliflower ear than to treat it, so make it a point to follow a few precautions.
- Whether you’re in the boxing arena or a rugby field, and whether it’s an international tournament or a practice session, always make it a point to wear protective head gear. While most competitive events require athletes and sportsmen to wear such gear, athletes tend to neglect safety during practice sessions. If you are engaged in any of the high-risk sports like boxing, wrestling, martial arts or water polo, always wear your head gear when you’re engaged in the sport.
- Make sure that your head gear fits you perfectly because an ill-fitted gear can often be just as big a problem as the actual trauma itself. The chin strap on your helmet should be snug enough so that your headgear does not get displaced each time there is contact.
- If its boxing or martial arts that you dabble in, keep in mind that you shouldn’t try to forcefully pull your head out of positions that you get caught and instead try to get out technically.
Health Tips
Here are some points that you should keep in mind:
- If you suffer from any kind of trauma to the ear, make it a point to get it checked at the earliest even if the injury seems minor.
- If it will take you time to get to your doctor, you can apply some ice and a head wrap until then. It would be a good idea to keep up the practice of applying ice for ten to fifteen minutes at a time for a few days more but make sure to keep a cloth between the ice and your skin.
- If you suspect an auricular hematoma or even if you are sure about it, do not attempt self-treatment. Attempting to drain the hematoma with a needle is not only ineffective but it also exposes you to a risk of infection.
- There is a higher likelihood of recurrence if drained at home as it is not possible to get all the fluid out.
- Avoid any activity that may cause trauma to the ear yet again until it has healed completely.