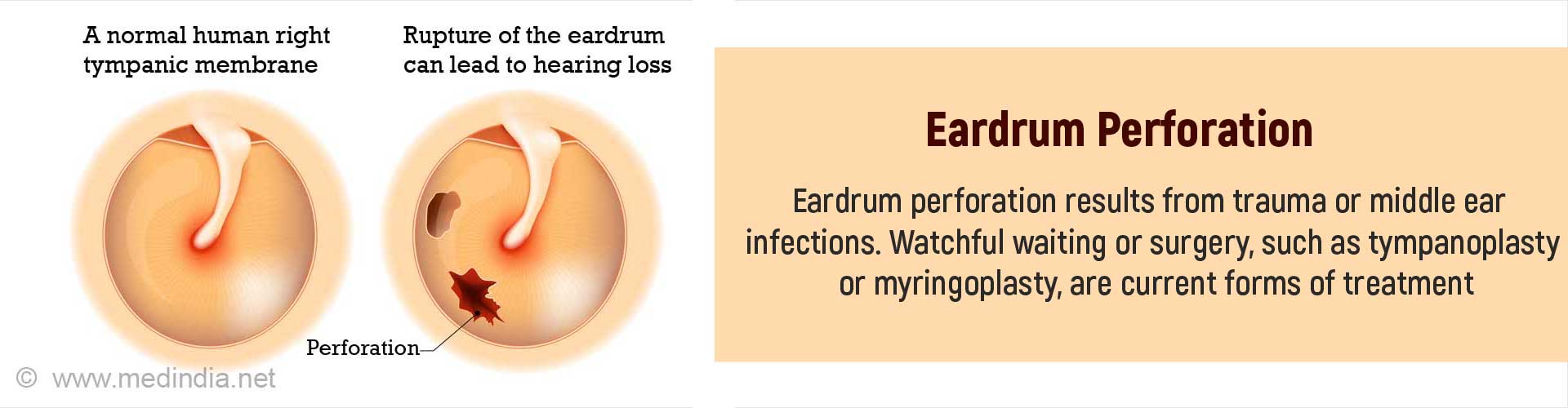
What are the Causes of Eardrum Perforation?
- Loud sounds – Explosions, gunshots
- Otitis Media – Infection of the middle ear (observed frequently in children)
- Barotrauma – Changes in air pressure due to scuba diving or flying
- Trauma – Head injury, slap on the ear, explosion, swelling of the ear tubes
- Accidental poking of the eardrum – Use of hair clips, cotton swabs, and matchsticks, most frequently, to remove earwax
- Fluid accumulation – Diving, calorie tests, squirting liquid with a syringe into the ear
- Surgical complications
- Removal of ear tubes – In rare instances, the ear tubes when removed could create a rupture in the eardrum
- Bone fractures

What are the Symptoms and Signs of Eardrum Perforation?
The most prominent symptoms of eardrum perforation are:
1. Hearing loss – Conductive
2. Cysts in the middle ear – Debris within the outer ear that is normally thrown out with the help of earwax may get lodged in the middle ear after the membrane gets perforated. The deposits of debris in the middle ear give rise to cysts or cholesteatoma.
3. Repeated infections – Infections in the middle ear (Otitis media) results in pus formation and this can cause a rupture or hole in the tympanic membrane. Due to the rupture of the eardrum, the middle ear is susceptible to external infections. If the infections do not resolve, you are likely to suffer from permanent hearing damage.
4. Pus or clear or blood-stained liquid secretions from the ear
5. Discomfort or earache
6. Buzzing noise in the ear (tinnitus)
7. Itching sensation in the ear