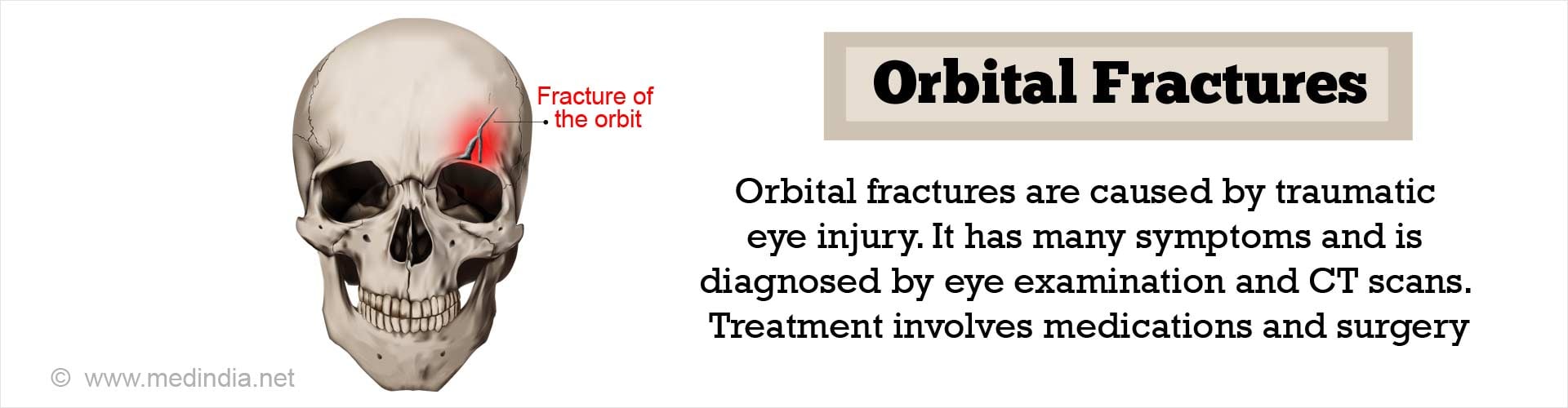
What are the Causes of Orbital Fractures?
Orbital fractures are primarily caused by any type of facial trauma. The most common causes of this type of trauma include the following:
- Motor Accidents: These are the most common cause of high-intensity orbital fractures. Cars are the most common motor vehicles involved in these accidents
- Violence: Interpersonal violence is the second most common cause of orbital fractures, following motor accidents. This can involve physical assaults such as a punch on the face
- Sports Injuries:
Sports-related injuries are an important cause of orbital fractures , especially in young adults. This may be caused, for example, by being hit by a cricket ball in the eye. It can also occur during contact sports such as boxing
What are the Symptoms & Signs of Orbital Fractures?
Symptoms and signs of orbital fractures usually depend on the type of fracture and the severity of the injury. The following symptoms are commonly observed:
- Pain: Fractures may cause severe pain in and around the eye. There may also be pain in the cheek while opening the mouth
- Swelling: Swelling around the eye is almost always present. In particular, swollen skin under the eye is very prominent. The cheek and forehead may also be swollen. Chemosis may occur, which is characterized by swelling or edema in the conjunctiva due to oozing of exudate from permeable capillaries
- Restricted Eye Movement: This usually occurs due to damage of some eye muscles within the fracture
- Blurry Vision: This occurs due to reduced visual acuity, which is a measure of the clarity of vision
- Ecchymosis: This is the discoloration of the skin due to bleeding underneath, resulting in black or blue colored bruises around the eye
- Bleeding: There may be bleeding in the white part of the eye. Hemorrhage under the conjunctiva (subconjunctival hemorrhage) may also occur
- Diplopia: This is commonly known as double vision. It usually resolves by itself within three to four days without any treatment
- Strabismus: This is characterized by an abnormal alignment of the eyes, resulting in a squint
- Hypoesthesia: There is a decreased sensation, which many manifest as numbness on the injured side of the face, including the cheek, eyelids, and mouth. This reduced sensitivity, which occurs due to nerve damage, may be temporary or permanent. Sometimes, there may be complete loss of sensation (anesthesia) around the eyes
- Enophthalmos: In this condition, the eye appears to be sunken within the orbit
- Exophthalmos: This condition is characterized by an excessive bulging or protrusion of eye
- Ptosis: This is the drooping of the upper eyelid
- Epiphora: This refers to excessive watering of the eye
- Teardrop Pupil: The pupil may become tear-shaped due to sudden increase in intraocular pressure by the force of the impact, resulting in rupture of the eyeball