Q: Which doctor should I see to consult on cervical cancer?
A: You should see a gynecologist or a gynecologic oncologist for your problem.
Q: I have a single sex partner. Do I need to do a pap test?
A: All women who are sexually active should undergo routine screening to prevent cervical cancer.
It is known that Cervical cancer is more common among women with multiple partners and also among women whose partners have several partners.
Q: Why does having multiple sex partners increase the incidence of cervical cancer?
A: The Human Papilloma Virus spreads through sex. The infection by this virus is very prevalent in the community and the current data from CDC estimates that about 20 million people in the U.S. are infected with HPV. Having multiple sex partners increases the chance of suffering from the infection and hence makes the women more prone to cervical cancer.
Q: At what age should Gardasil (human papillomavirus vaccine) be administered?
A: The FDA has approved Gardasil for girls and women between 9 and 26 years.
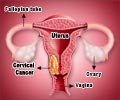
Q: If my mother had cervical cancer - Do I have risk of this cancer?
A: Cervical cancer is caused by many factors. Unlike breast cancer which can be inherited cervical cancer is not known to be inherited.
Q: Is cervical smear or Pap smear painful?
A: No Pap smear test is not painful. There may be mild discomfort and light spotting for a day or two. If the procedure is painful or the spotting heavy - you should make sure there is no underlying infection.
Q: Is the Pap smear very accurate in detecting cancer?
A: Yes Pap smear is very reliable. However no test is 100% foolproof. Many labs follow a double reporting system to check for errors.
Q: Which age group of women are more prone to cervical cancer?
A: In India ,cervical cancer peak age incidence is in the early 50’s. Cervical cancer is extremely rare in women younger than age 20.
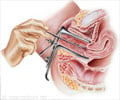
Q: What should I know about screening for cervical cancer?
A: The Pap test is recommended for women aged 21-65 years old. The Pap test only screens for cervical cancer. A Pap test is a procedure to collect cells from the surface of the cervix and vagina. A piece of cotton, a brush, or a small wooden stick is used to gently scrape cells from the cervix and vagina.
Q: How often should I be screened for cervical cancer?
A:
- Women ages 21 - 29 should be screened once every 3 years with a Pap test.
- Women ages 30 - 65 should be screened with either a Pap test every 3 years OR a Pap test and HPV test every 5 years.
- Women age 65 and older no longer need Pap tests as long as they have had regular Pap tests with normal results. Women who have been diagnosed with pre-cancer should continue to receive regular screenings.
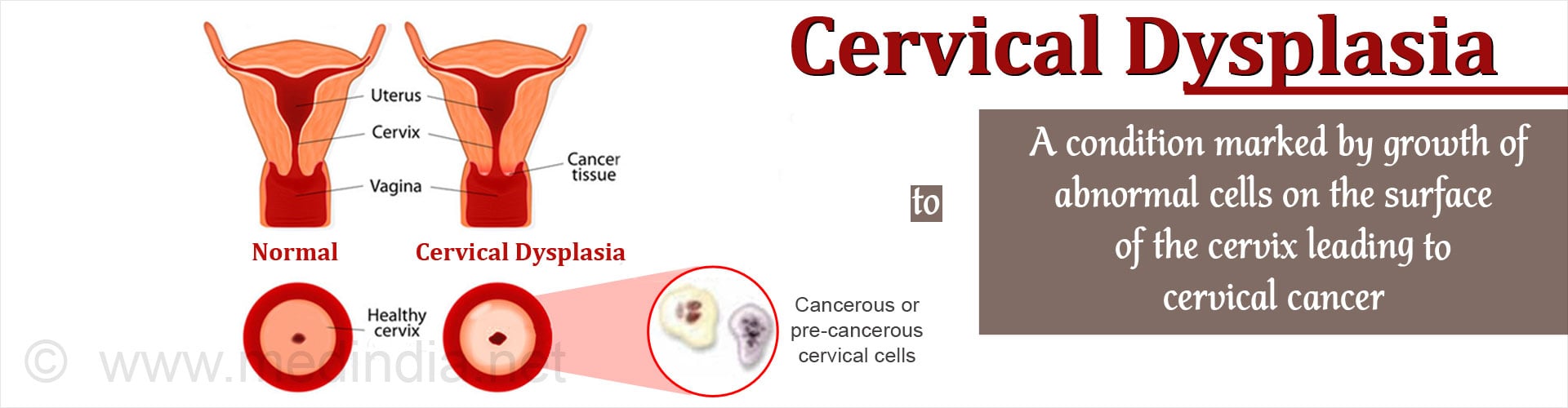
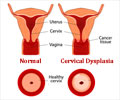
Q: What can cause precancerous cells in the cervix?
A: Cervical dysplasia is the abnormal growth of precancerous cells on the surface of the cervix. The precise cause of cervical dysplasia is not known. Studies have found a strong association between cervical dysplasia and HPV infection. Without treatment, 30 to 50% of cases of severe cervical dysplasia progress to invasive cancer.
Q: How can I lower my chances of getting cervical cancer?
A:
- Do not smoke.
- Limit your number of sexual partners or use condoms in such situations.
- Get an HPV vaccination
- Get a regular Pap smear.
- Maintain good vaginal hygiene
Q: Is cervical cancer infectious?
A: The cancer itself is not contagious.
Q: Is cervical cancer curable?
A: The prospect of a complete cure is good for cervical cancer diagnosed at an early stage, although the chances of a complete cure decrease, the further the cancer has spread.
Q: After a radical hysterectomy will I be able to have sex?
A: Yes, you will be able to have intercourse, usually without any difficulties, because the vaginal tissues are very stretchy. If you encounter problems you can schedule an appointment with your gynecologist.
Q: Will I be able to have children after treatment for cervical cancer?
A: It depends on how early the cancer is detected. The earlier the cancer is found, the more higher the chances are to preserve your fertility.