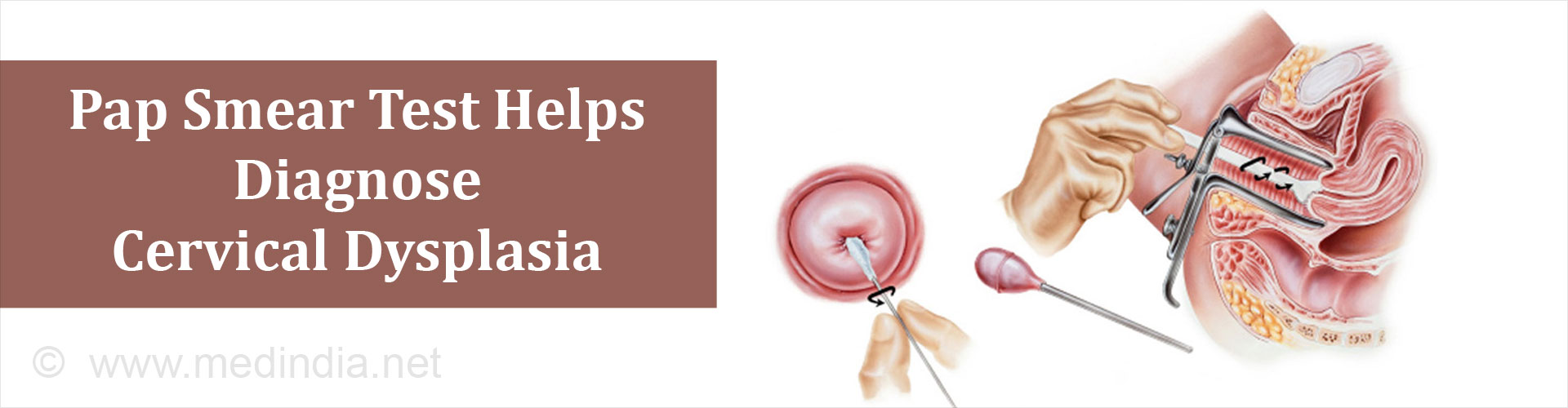
Q: Which doctor to consult for cervical dysplasia?
A: Consult a gynecologist, who may refer you to an oncologist for further treatment.
Q: What is prognosis of cervical dysplasia?
A: Cervical dysplasia has good prognosis. 70% of mild dysplasias resolve on their own and rest of the 30 % get cured by timely and appropriate treatment and regular follow up.
Q: How is HPV transmitted?
A: HPV is mainly transmitted through sexual contact. Hand to genital transmission, mouth to genital transmission and transmission from mother to baby during vaginal delivery can also occur. The virus is not found in blood or body fluids.
Q: How can HPV be prevented?
A: As HPV is sexually transmitted, abstinence from sexual activity is the only method to prevent it. Use of condoms can decrease the spread of HPV but not completely prevent it. Spermicides and hormonal contraception do not prevent HPV.
Q: Can genital warts make you infertile?
A: Genital warts will not make you infertile. You can have normal pregnancy and deliver vaginally too. In very rare cases, the virus can spread to the baby during delivery. If the warts are too big, then you may need to undergo Caesarean Section.
Q: Can genital warts cause cancer?
A: HPV types 6 and 11 causing genital warts will not cause cancer of cervix, vulva, penis or anus.
Q: Can cervical dysplasia make you infertile?
A: Cervical dysplasia by itself will not make you infertile, but you stand a higher chance of contracting other sexually transmitted diseases like Chlamydia which can cause infertility.
Q: Can dysplasia occur even after hysterectomy?
A: Yes, it can occur after hysterectomy on the vaginal walls. Hence you need to get regular Pap smear of the vaginal walls.