Symptoms and Signs of Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD)
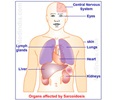
Most of the patients with CGD present during the first 5 years of life. The most commonly involved organs are: skin, lungs, GI tract, lymph nodes, liver, and spleen.
An early onset of severe recurrent bacterial and fungal infections may be referred to as the clinical hallmark of chronic granulomatous disease. Most of the patients with CGD present during the first 5 years of life. The most commonly involved organs are: skin, lungs, GI tract, lymph nodes, liver, and spleen.
Common presentations include:
- Skin infections
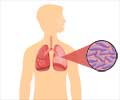
- Pneumonia (Respiratory disease characterized by inflammation of the lung tissue)
- Lung abscesses (collection of pus)
- Inflammation of lymph nodes (Suppurative lymphadenitis)
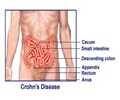
- Diarrhoea (due to Inflammation of the intestine, i.e. enteritis)
- Perianal or perirectal abscesses (collection of pus in the adjacent areas of anus or rectum)
- Abscesses in liver or spleen
- Inflammation of bones (osteomyelitis) and septicemia (Invasion of the bloodstream by infective microbes) can also be presenting features of the ailment.
Up to 20% of patients with chronic granulomatous disease suffer fungal infections. They may be locally invasive or disseminated. Aspergillus species is the culprit in most of the cases.
Another characteristic feature is an excessive accumulation of immune cells into aggregates called granulomas.
Granulomas most commonly affect the skin, gastro intestinal tract (GI), and genitourinary (GU) tract. Hence some patients with CGD present with symptoms related to obstructions produced by granulomas in the GI tract or GU tract. These include: abdominal pain, diarrhoea, nausea and vomiting, bloody diarrhea and constipation.
General health or constitutional symptoms are not associated with chronic granulomatous disease. Unexplained fevers may occur however.
Chronic or recurrent infections affect the growth of children, resulting in failure to gain weight (failure to thrive).
Common infections that demand detailed work up for CGD include: Aspergillus, Nocardia or Burkholderia cepacia pneumonia, a staphylococcus liver abscess or pneumonia, or a bone infection with Serratia marcescens.