Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia - Diagnosis
Most often chronic lymphocytic leukemia is diagnosed accidentally while testing for another medical condition. It can be diagnosed by a simple blood test and by carefully evaluating the symptoms.
Once CLL is suspected, certain specific tests need to be undertaken by the affected individual in order to confirm the diagnosis.
It has now been discovered that there may be at least two types of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. One kind is a smoldering, rather a slow-progressing type, that normally does not require treatment. The other is a more aggressive variety, which is a more serious disease.
With these developments, doctors now believe in doing more tests, besides the conventional blood test, to ascertain the diagnosis. These tests will give the doctor an idea as to the progression of the disease.
The following are some of the diagnostic tests for CLL -
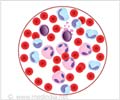
Blood Test- There is an increased number of lymphocytes in patients with CLLca. The number of RBCs and platelets are abnormal too. However, they look normal when seen through the microscope hence further tests, such as Cell Typing or Immunophenotyping, are required to confirm the diagnosis.
Cell typing helps to confirm if the increased number of lymphocytes are caused by cellular reaction to an inflammation or due to cancer. It also helps to identify CLL from other types of leukemia.
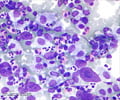
Bone Marrow Test- This test is usually done to confirm a diagnosis and to rule out other related diseases. A bone marrow test is not an absolute requisite and is carried out rarely to diagnose CLL.
For this test, a small amount of bone marrow is aspirated from the pelvic bone or sternum (breast bone) using a needle. Local anesthesia is employed to carry out the procedure. The aspirated sample is observed under the microscope to check for abnormal cells. It can also be used for other tests, such as cell typing or cytogenetic testing.
Cytogenetic Tests- These tests are carried out to detect changes, such as the deletion or a translocation, in the chromosomes. Special techniques, like Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (
Certain substances in the individual may indicate a more severe form of the disease. These are high amounts of the proteins ZAP-70, immunoglobulin mutation status or CD38.
Other tests, such as chest x-ray, are performed to assess the overall health status of the individual.