Crohn's Disease - Symptoms
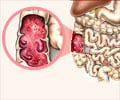
Crohn’s disease may affect any part of the digestive system from mouth to anus, but it has a predilection to the small bowel. Within the small bowel, it may affect the last portion, namely the ileum alone or the entire jejunum and ileum or involve the colon in addition to the small intestine. The colon is not always affected, although there may be peri-anal abscesses, fistulae, as well as anal fissures.
Symptoms of Crohn’s disease depend on the location of the ulcers or sinuses.
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea are the common features, wherever the disease is located.
- Bleeding may sometimes occur.
- Severe crampy pain with vomiting and dehydration may occur with a perforate or acute abdomen.
- Fever, pain and discharge of pus and mucus may happen if there is a peri-anal abscess.
- A fistula that ends in a blind space in the abdomen can lead to a pus collection called abdominal abscess.
- Weight loss is a common feature as these people often suffer from repeated attacks of diarrhea that leads to malnutrition.
- Crohn’s disease symptoms also include extra intestinal manifestations such as uveiitis (red eye), arthritis, sacro-illiitis, and skin nodules, ankylosing spondylitis and sclerosing cholangitis. Therefore, the patient may have back pain, red-eye, hip pain, jaundice even cirrhosis of the liver.
Complications of Crohn’s disease range from abscess formation, adhesions of the intestine to nearby structures to abnormal communications between adjacent organs like the urinary bladder, vagina and skin due to the process of inflammation, perforation and obstruction. These are known as fistulae or sinuses when the tunnel-like communication opens into the skin.