Glossary
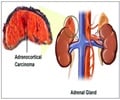
1. Adrenal Glands:A pair of small glands, one located on top of each kidney. The adrenal glands produce sex hormones and hormones that help control heart rate, blood pressure, the way the body uses food, and other vital functions.2. Adenoma: General term for a benign tumor of a gland.
3. Benign: Not cancerous; does not invade nearby tissue or spread to other parts of the body.
4. Bursitis: Inflammation of a bursa due to excessive pressure or friction, or from injury.
5. CT-Scan: Computerized Tomography Scan.
6. Cortisol:The major natural glucocorticoid (GC) in humans. It is the primary stress hormone.
7. Corticosteroids: Hormones produced by the cortex of the adrenal glands; also, synthetic hormones used as medications.
8. Diabetes: A condition in which the body cannot properly store or use glucose (sugar), the body's main source of energy.
9. Lupus: Lupus is an autoimmune disease and a chronic inflammatory disease, affecting body parts like the kidneys, skin, heart, joints and even the lungs.
10. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): A painless method using magnetic fields for taking pictures of internal organs.
11. Malignant: A cancerous growth that may destroy nearby normal tissue and spread to other parts of the body.
12. Metastasis: Transfer of disease from one organ or part of the body to another, the causative agent having been conveyed by the blood or lymph.
13. Obesity: Over weight
14. Osteoporosis: A disease in which bones become thin, weak and are easily fractured.
15. Rheumatoid arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease of the connective tissues that usually appears in the form of painful swelling in the joints of the hands and feet. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) often worsens over time, causing joint deformities and disability.