- Deviated Septum - (https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/deviated-septum)
- Deviated Septum / Polyps - (https://www.desertent.org/deviated-septum-polyps/)
- Deviated Septum - (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16924-deviated-septum)
- Deviated nasal septum. Incidence and etiology - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/99070/#)
- Use, Abuse, and Misuse of Nasal Medications: Real-Life Survey on Community Pharmacist's Perceptions - (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10142332/)
About
A deviated septum happens when the thin wall that divides your nostrils leans to one side, leading to uneven airflow in the nasal passages. Although it may appear to be a minor structural problem, it can greatly affect daily life. Common consequences include sleep issues, decreased physical activity, and other unforeseen complications. Understanding its causes and symptoms is essential for effectively managing and treating this condition(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Deviated Septum
Go to source).
Did You Know?
Over 80% of people have some degree of nasal septum deviation! #deviatedseptum #medindia
What Happens When the Nasal Septum is Misaligned?
When the nasal septum is not properly aligned, it can interfere with normal airflow, resulting in complications like obstructed airflow that may cause partial or complete blockage of one or both nostrils. This misalignment can also hinder sinus drainage, raising the likelihood of chronic sinusitis and respiratory infections due to ineffective nasal function.
Furthermore, structural problems such as nasal polyps or chronic rhinitis may arise, and in more severe instances, this condition can lead to sleep apnea, which causes interruptions in breathing during sleep(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Deviated Septum / Polyps
Go to source).
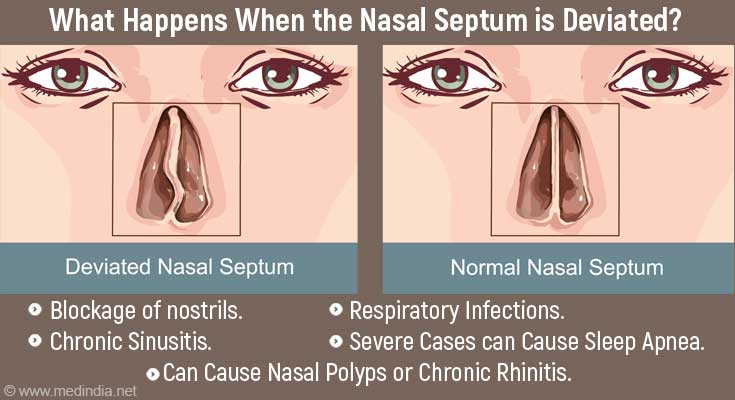
How to Tell if You Have a Deviated Septum
Lean your head back and take a look in the mirror. (You can also snap a photo of the underside of your nose.) If your nostrils appear uneven or are different sizes, you might have a deviated septum.
You can also try this simple self-test for a deviated septum:
- Using your finger, close one of your nostrils.
- Breathe in and pay attention to the airflow. Notice how easy or hard it is to breathe through that nostril.
- Next, close your other nostril and do the same thing.
- If you find it difficult to breathe through one or both nostrils, it could indicate a deviated septum(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Deviated Septum
Go to source).
While this test can be a useful tool, the only definitive way to determine if you have a deviated septum is to consult a healthcare professional.

What Causes a Deviated Septum?
A deviated septum can result from several factors, such as:
- Genetic Predisposition: Some people inherit a tendency for nasal structural issues.
- Nasal Trauma: Injuries sustained from sports, accidents, or fights can affect the nose.
- Developmental Issues: Abnormal growth during childhood can lead to changes in nasal structures.
- As the nose develops, the septum can also grow and may lean to one side, which is the most frequent cause of a deviated septum(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Deviated nasal septum. Incidence and etiology
Go to source).
Understanding these risk factors aids in early detection and better management.
Symptoms of a Deviated Septum
A deviated septum can impact your daily life in several ways:
- Respiratory Issues: When airflow is blocked, it can lead to mouth breathing, a dry mouth, and worsen existing respiratory problems. This condition may also result in noisy breathing (stridor) and nasal congestion.
- Chronic Sinus Infections: Ineffective sinus drainage can encourage bacterial growth, leading to sinus inflammation and infections that cause facial pain and persistent congestion.
- Sleeping Disorders: Conditions like snoring or sleep apnea can interrupt sleep, resulting in fatigue, irritability, and decreased concentration.
- Loss of Smell and Taste: Blocked airflow can reduce your ability to smell and taste.
- Reduced Physical Activity: Breathing difficulties through the nose can limit your ability to exercise and engage in physical activities.
- Recurrent Nosebleeds: Uneven airflow can dry out and crack nasal membranes, leading to frequent nosebleeds.
- Headaches and Facial Pain: Sinus pressure and inflammation can trigger chronic headaches.
- Voice Changes: Alterations in the nasal cavity can impact voice resonance, which is particularly concerning for those who rely on their voice professionally.
How a Deviated Septum Affects Breathing and Quality of Life
A deviated septum can block airflow through one or both nostrils, significantly impairing breathing and affecting oxygen intake. This reduced oxygen flow can lead to poor sleep quality, as individuals may experience disrupted breathing or conditions like snoring and sleep apnea.
The limited airflow also restricts physical activity by decreasing exercise capacity, causing individuals to feel chronically fatigued and less energetic throughout the day. Over time, this ongoing fatigue can lead to irritability, difficulty concentrating, and a decline in overall mental and emotional well-being.
To manage symptoms, people might resort to over-the-counter decongestants or nasal sprays. However, relying on these medications for an extended period can result in rebound congestion, worsening symptoms, and creating a cycle of dependency. Without appropriate treatment, quality of life can be significantly impacted, underscoring the need for medical evaluation and possible interventions, such as surgical correction, to effectively address the problem(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Use, Abuse, and Misuse of Nasal Medications: Real-Life Survey on Community Pharmacist's Perceptions
Go to source).
Diagnosing a Deviated Septum
An ENT specialist can diagnose a deviated septum through several methods:
- Physical Examination: The doctor employs a nasal speculum, a small tool that gently opens the nostrils, to visually examine the inside of your nose. They look for any visible misalignment, bumps, or irregularities in the septum.
- Symptom Assessment: This involves reviewing your medical history and any symptoms you may be experiencing.
- Imaging Studies: CT scans might be utilized for a more detailed view, especially if surgery is being contemplated.
Treatment Options for a Deviated Septum
Conservative Management:
For mild to moderate cases, non-surgical treatments aim to relieve symptoms and enhance nasal function.
Nasal Corticosteroids:
Prescription sprays help reduce inflammation and decrease swollen nasal tissues, which improves airflow. It may take several weeks to notice results, and they should be used consistently.
Decongestants:
These provide temporary relief from nasal congestion by constricting blood vessels. They are intended for short-term use only to prevent rebound congestion, where symptoms can worsen after stopping.
Saline Nasal Sprays:
Available over-the-counter, these sprays keep nasal passages hydrated, clear mucus, and alleviate dryness and congestion in a gentle manner.
Surgical Interventions:
If conservative treatments are ineffective or the deviation is significant, septoplasty is the primary surgical option. This procedure involves realigning or removing the deviated septum to restore airflow and alleviate symptoms such as snoring or sinus infections. Septoplasty is usually performed under local or general anesthesia, with recovery lasting from a few days to a few weeks.
Septoplasty:
The surgeon straightens or removes the deviated septum through an incision inside the nostrils. In some cases, additional surgeries like rhinoplasty or sinus surgery may be combined if needed. If nasal polyps are present, polypectomy may also be performed alongside septoplasty.
The decision between conservative management and surgery depends on the severity of symptoms and their impact on quality of life. A thorough evaluation by an ENT specialist is essential for determining the best treatment plan.