Q: Which doctor should I consult in the case of diabetes insipidus?
A: An endocrinologist can diagnose and treat diabetes insipidus.
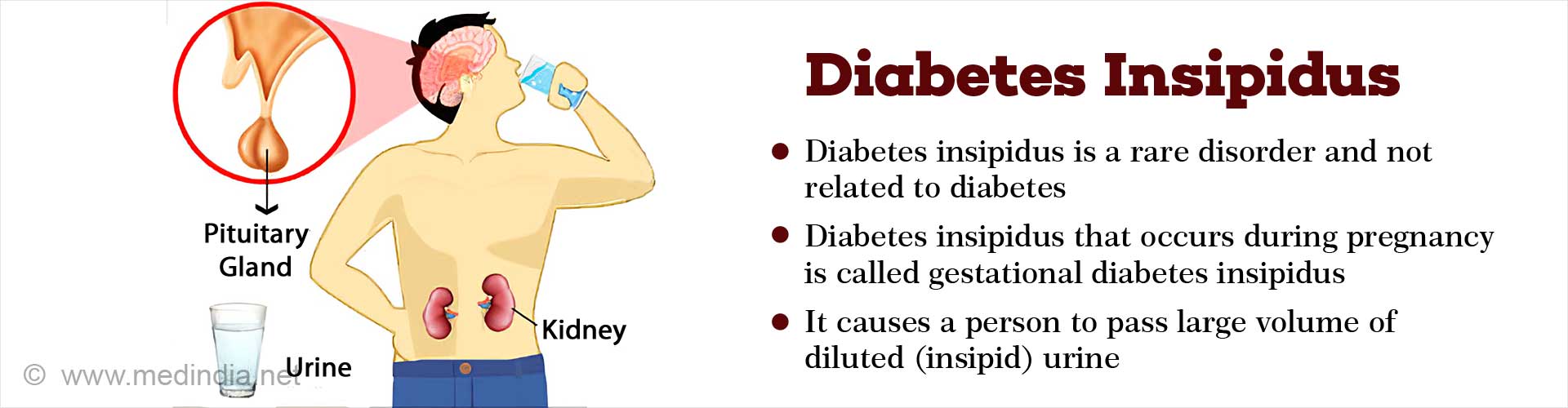
Q: What is neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus?
A: This is another term for central diabetes insipidus. Neurohypophysis is another name for the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland which is responsible for the secretion of ADH.
Q: Why does gestational diabetes insipidus?
A: Gestational diabetes insipidus occurs during pregnancy due to an increase in the breakdown of ADH.
Q: Is Vasopressin / Desmopressin (DDAVP). ) safe for treatment of Diabetes Insipidus?
A: Yes it is considered a safe medication. It is the first line drug to treat central diabetes insipidus
Thedesmopressin (DDAVP) is easy to administer and welltolerated.
The major complication of desmopressin treatment is water intoxication and low sodium or hyponatremia and this can be reduced by first starting with a low dose and closely monitoring blood sodium and osmolality level.
Q: Can Diabetes Insipidus be Life Threatening?
A: If recognised early it has excellent outcome to treatment but if not recognised and it becomes severe; it can lead to dehydration and become life threatening.
Q: Can Diabetes Insipidus be cured?
A: There's no known cure for Diabetes Insipidus, however the treatment can help control it and take care of its symptoms like reduce excess urine formation and thirst.
Q: Can I drink alcohol if I have Diabetes Insipidus?
A: Alcohol normally reduces secretion of the hormone vasopressin. Hence if you have Diabetes Insipidus, you should avoid drinking alcohol. A small social drink maybe alright but large quantities is a strict no.