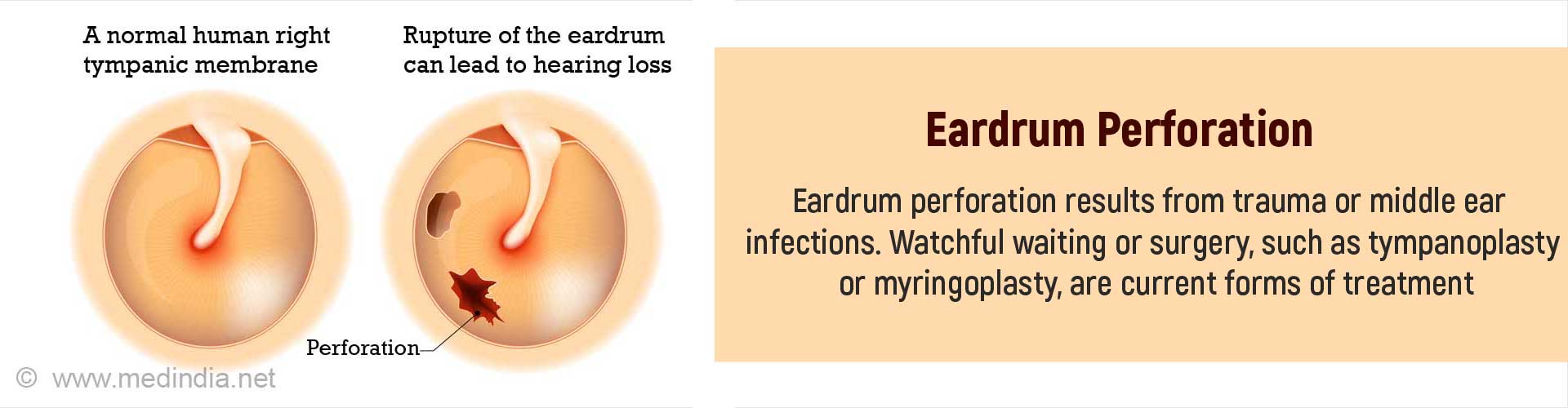
How do you Diagnose Eardrum Perforation?
- Your family doctor or an ENT (Ear, Nose and Throat) specialist will take a medical history to determine if you have had fever or experienced any trauma recently.
- They will use a small torch with a magnifying lens, the otoscope,to examine the ear. If there is no pus or other discharge, the perforation in the eardrum will be seen.

- If there is pus, it may be aspirated for carrying out laboratorytests to detect bacterial infection.
- To as certain hearing loss, you may have to go through audiometry or hearing tests. These tests will measure how well you hear different sounds, pitches, and volumes.
- Tympanometry measures the reaction of the eardrum to slight air pressure changes.
- Vibrations of tuning forks will be used to detect the extent of hearing loss and the region of the ear that is affected.
How do you Treat Eardrum Perforation?
The traditional and conservative method to treat eardrum perforation involves patiently waiting for the hole to heal. Sometimes,antibiotics (Ofloxacin or Floxin) are recommended for recent infections and it is best to avoid any fluid or water entering the ears. When the perforation fails to heal within 6 months, resulting in chronic ear infection, surgery may be considered to repair the perforation.
Middle ear infection can result in complications,such as facial paralysis, vertigo orextreme cases of hearing loss. This is the time when surgery is considered as treatment.
There are two main surgical procedures to treat eardrum perforation. The aim is to close the perforation with the intent of restoring the structure and function of the eardrum.
Tympanoplasty: This is an outpatient procedure where tissue such as cartilage, fat, fascia (lining of muscles), and perichondrium from your body is used to patch up your eardrum. Sometimes, synthetic substances like paper patch or silk fibroin membranes are used to patch the eardrum. The surgeon accesses the eardrum through the back of the ear or through a cut in the ear canal. The eardrum is lifted and patched with the selected material.The surgery may take around 2-3 hours. This procedure is used for recurrent or large perforation problems. Besides the eardrum, the structure behind the membrane that transmits sound to the inner ear is also repaired.
Myringoplasty: This surgical procedure involves placing specialized paper or a gel over the eardrum. This is a minor procedure and is completed within half an hour.
Tissue engineering now appears to be a useful alternative to the above surgical approaches, as revealed by new research studies. Novel materials, such as bio molecules and polymer scaffolds are showing promising results in the treatment of eardrum perforation.