Diagnosis of Hairy Cell Leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia is diagnosed using blood and bone marrow tests.
If the symptoms of the patient suggest that the patient has leukemia, the doctor needs to do further tests to confirm the diagnosis. Tests used in the diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia include:
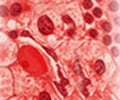
- Complete blood count (CBC): When observed under the microscope, following abnormalities may be noted:
- Reduced numbers of normal red and white blood cells, and platelets
- Increased number of white blood cells in some individuals due to a high number of hairy cells
- Peripheral Blood smear: Examination of the abnormal cells under a microscope reveals fine hair like cytoplasmic projections.
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy: Bone marrow aspiration often results in dry taps due to lack of adequate cells. A bone marrow biopsy helps to clinch the diagnosis. Immunological tests are also carried out on the blood and bone marrow samples to identify antigens on the cells.
- Spleen and Liver:Biopsy of liver and spleen reveals infiltration of cancer cells in the tissues.
- Genetic tests:Genetic tests are carried out to study the patient’s abnormalities in the genes that increase the risk for the leukemia.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging studies such as chest X-ray, bone scan, CT scan, MRI, and ultrasound are usually done to look for conditions like enlarged spleen and infections.