Diagnosis of Uterine Polyps | Endometrial Polyps
A detailed gynecological history and examination along with certain tests are used to diagnose uterine polyps.
Diagnosis of uterine polyps is made based on the following:
- A detailed menstrual history may raise the suspicion of the presence of uterine polyps. Information about difficulty in getting pregnant or history of miscarriage should be sought.
- A complete gynecological examination is necessary.
- Tests and procedures are used in the diagnosis of uterine polyps include:
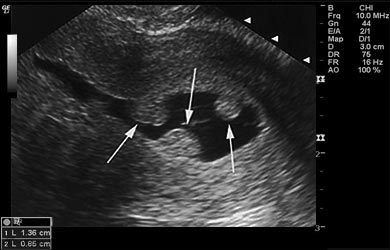
Ultrasound: Ultrasound may be used in the diagnosis of uterine polyps. In transvaginal ultrasound, an ultrasound transducer is inserted in the vagina to obtain an image of the interior of the uterus and detect the presence of any polyps. This procedure may be followed by a hysterosonography, wherein saline is introduced into the uterus through a small tube or catheter. The saline solution expands the uterine cavity, thereby giving a clearer picture of any overgrowths inside the uterus.
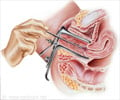
Hysteroscopy: This procedure can be used both in the diagnosis and treatment of uterine polyps. In this procedure, a lighted telescope, also known as the hysteroscope, is inserted in the uterine cavity through the vagina and cervix. Thus, the inner lining of the uterus can be directly visualized and any polyp can be detected. The polyp may be removed in the same sitting using an instrument called a curette.