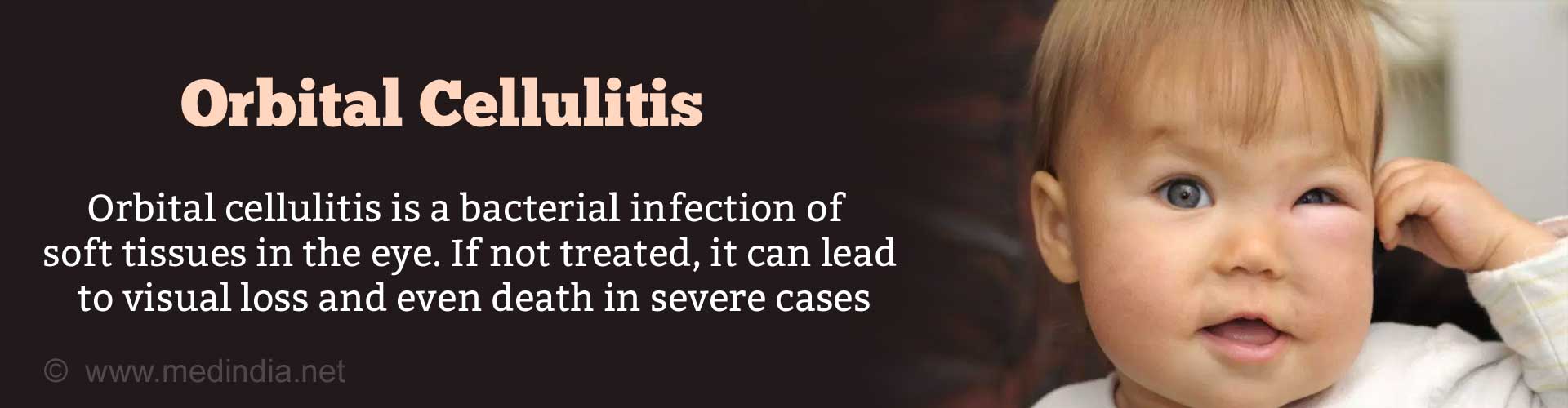
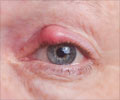
How do you Diagnose Orbital Cellulitis?
The diagnosis is based on clinical examination. Typical symptoms like difficulty in moving the eyes in different directions, pain with eye movement, along with raised white cell count and fever support the diagnosis.
The physical or clinical examination includes:
- measuring intra-ocular pressure (IOP)
- examination of the eye using slit-lamp microscope
- examination of dilated fundus (fundoscopy)
- assessment of color vision to evaluate optic nerve damage
Other tests could be done to further confirm the diagnosis including
- Blood culture to identify the causative organism
- CBC (Complete Blood Count)
- Spinal tap (lumbar puncture), in children, who are very sick to rule out brain infection
Further tests may also include:
- Microbial culture of eye or nasal discharge
- X-ray of the sinuses
- MRI or CT scan of the orbit or sinuses
How can you Treat Orbital Cellulitis?
It is important to treat orbital cellulitis immediately. Depending on the severity of infection, hospitalization and frequent observation may be required.
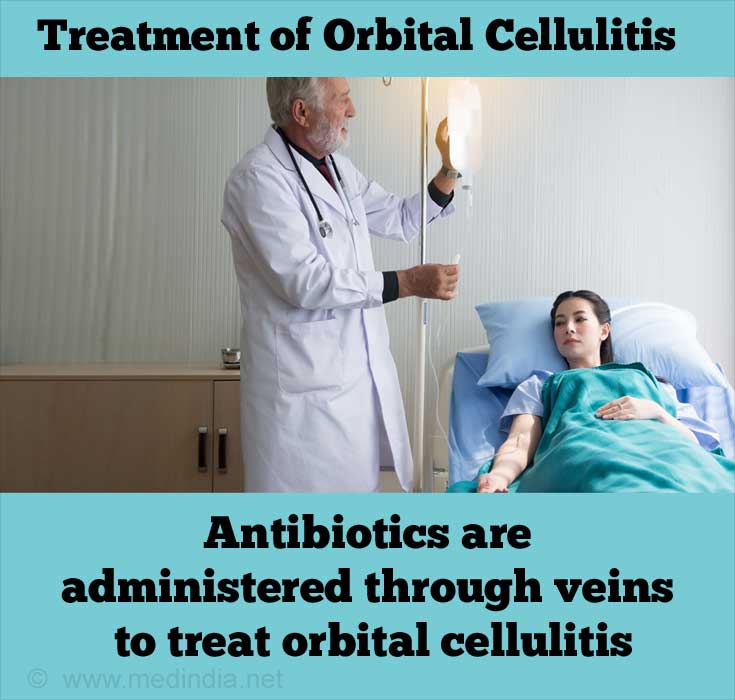
Antibiotic therapy
Treatment generally includes giving antibiotics like penicillins or cephalosporins, via intravenous route.
Blood, throat or nasal cultures help in prescribing the suitable antibiotic.
Surgical intervention
Surgery may be needed in some cases, as it can lead to vision loss or affect neurological status of the patient. Surgery helps to drain the sinuses to relieve pressure in space around the eye.
A person severely affected must be under critical observation, every few hours.
In many cases, co-management of patient between ophthalmology surgeon, ENT and pediatrician (child specialist) would be required.
How to Prevent Orbital Cellulitis?
Patients suffering from upper respiratory or sinus infections must be treated immediately to reduce the risk of developing orbital cellulitis
Children must be given HiB vaccine shots to prevent Haemophilus influenzae bacterial infection
Young children staying with a person suffering from this infection must be given prophylactic antibiotics to prevent getting the same infection
Any dental infection must be treated immediately to prevent further spread that may lead to orbital cellulitis