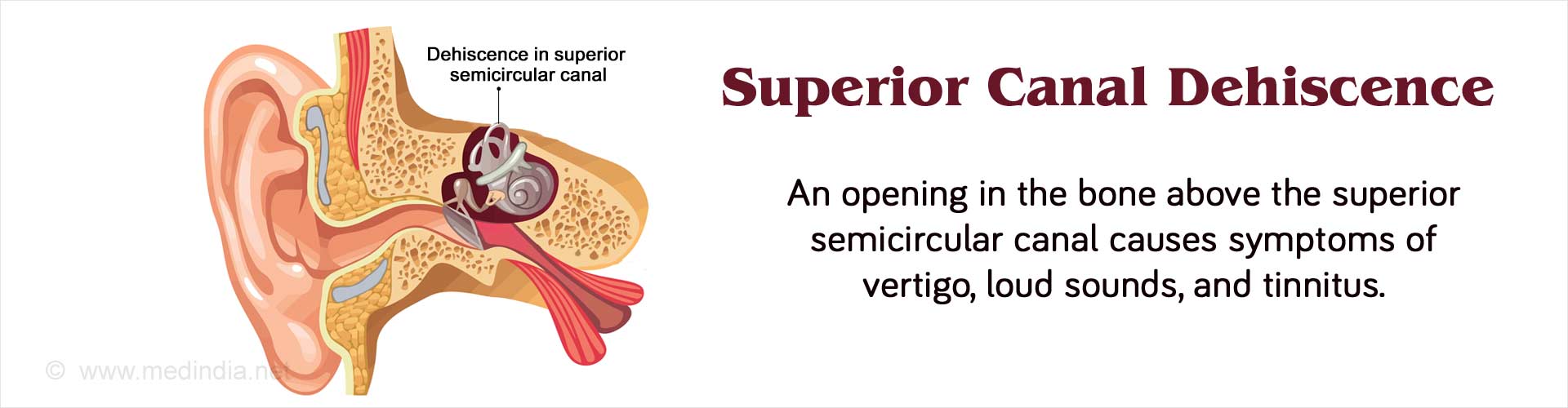
How do you Diagnose Superior Canal Dehiscence?
The general age to diagnose SCD is 45 years. Diagnosis of SCD is conducted based on the following tests:
- Clinical Examination: In this case, an audiometer is played at different frequencies near the ear and eye movements are monitored. If the eyes move in the zone of the superior semicircular canal, then SCD is confirmed
- Electrocochleography (ECOG): In this procedure, the conducting electrical potential of sound through the vestibule is measured. A hole in the bone can cause a change in the conducting potential and this is reflected in the ECOG output
- Imaging: Computed tomography (CT) scanning is useful to detect the opening in the bone above the superior semicircular canal. However, it is possible for CT scans to miss a thin bone and give a wrong diagnosis. Only centers experienced in diagnosing SCD should be accessed for CT scans
- Vestibular-evoked Myogenic Potentials (VEMPs): This is an important test for confirming SCD because the sound wave is amplified more through the vestibule in SCD than when bone dehiscence is absent
- Audiometry: Acoustic reflex testing distinguishes hearing loss symptoms and confirms SCD
In order to diagnose SCD, one has to meet certain requirements, which include the following:
- Display of one of the SCD-related symptoms
- Computed tomography (CT) scans showing the bone rupture in high resolution
- Evidence of a third window in the inner ear through one of the following diagnostic findings:
- Proof of irregularity in conducting potential within the ear when there is no obvious hearing loss
- Bone conduction of sound is affected in audiometry tests
- Conduction of electrical potential through the vestibule is increased
How do you Treat Superior Canal Dehiscence?
Treatment of SCD is performed based on the symptoms and can involve any of the following approaches:
- Medications: In those who display symptoms of autophony or tinnitus, diuretics can help reduce the CSF pressure, which alleviates the associated symptoms
- Tympanostomy Tube: Those who display symptoms due to pressure changes, a tympanostomy tube helps to reduce the symptoms
- Surgery: Surgical intervention is utilized to seal the opening in the bone above the superior semicircular canal. There are different surgical techniques to achieve this purpose. They are as follows:
- Transmastoid approach
- Reinforcement of the round window
- Repair of the middle cranial fossa with the help of endoscopy
- Plugging or capping
How to Prevent and Manage Superior Canal Dehiscence?
In general, once SCD is diagnosed, those affected may choose to avoid the stimuli that trigger the symptoms. In some cases, this helps. In other cases, when the symptoms fail to cease, then surgery or other medical treatments are recommended. Effective diagnosis is key to managing SCD.