About
Diverticulosis is characterized by sac-like outpouching in the intestinal wall. Inflammation of diverticula results in diverticulitis.
Diverticulosis is a condition where sac-like outpouching develops in the intestinal wall. Intestinal diverticula may be true or false. In a true diverticulum, all the layers of the intestine form the diverticulum. In false or pseudo-diverticulum, only the innermost layers, i.e. the mucosa and the submucosa herniate out through the muscle layers at a weak point in the muscle. False diverticula are more common than true diverticula.
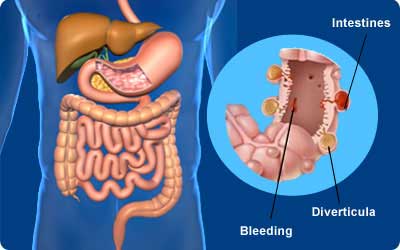
Diverticulosis affects both males as well as females, usually above 60 years of age. The sigmoid colon or the last part of the large intestine just before the rectum is commonly affected in the Western population. However, the right side of the colon is more commonly affected in Asians.
Conditions that increase a person’s risk to develop diverticular disease are:
- Diet low in fiber, high in fat and red meats: A westernized diet with low fiber and high fat is particularly notorious in causing diverticulosis
- Constipation
- Obesity increases the chances of developing diverticulosis especially in young individuals
Inflammation of a diverticulum is called diverticulitis. It often occurs due to accumulation of fecal material in the diverticulum.
Diverticulosis may cause blood in stools. The bleeding usually stops on its own without any treatment.
Uncomplicated diverticulitis may cause symptoms like fever, pain in abdomen, severe constipation or loss of appetite. The patient may suffer from complications like perforation, abscess, stricture or fistula formation.
Diverticulosis may also affect the small intestine, though less commonly than the large intestine. Among small bowel diverticula, a true diverticulum called the Meckel’s diverticulum is most common. It occurs due to a developmental abnormality in the fetus. It may result in complications like bleeding, intestinal obstruction, diverticulitis, ulcer and rarely tumor formation.
Diverticulosis is diagnosed using colonoscopy and mesenteric angiography. Diverticulitis is diagnosed with the help of CT scan.
Patients with diverticulosis are treated with a high fiber diet and drugs that reduce spasm for pain. Diverticulitis is treated with antibiotics and bowel rest. Abscesses are treated with antibiotics and surgical drainage. Other complications like perforation, strictures and fistulas may need surgery.