- Ear deformities - Children’s Hospital of Philadephia, USA - (https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/ear-deformities)
- Junior AT, Haetinger RG, de Carvalho e Silva FL, de Castro Gudmon M. Middle and inner ear malformations in two cases of velocardiofacial syndrome. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009; 13(1): 83-6.
- Facts about Anotia/Microtia - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, USA - (https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/anotia-microtia.html)
- Bartel-Friedrich S, Wulke C. Classification and diagnosis of ear malformations. GMS Curr Top Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 6: Doc05.
- Cox TC, Camci ED, Vora S, Luquetti DV, Turner EE. The genetics of auricular development and malformation: New findings in model systems driving future directions for microtia research. Eur J Med Genet. 2014; 57(8): 394-401.
- Franchella A, Pellegrinelli S, Carinci F, Zollino I, Carnevali G, Candotto V, et al. Congenital malformations of the ear. Eur J Inflamm. 2012; 10 (1): 35-8.
- Woo JE, Park Y-H, Park EJ, Park KY, Kim SH, Yim S-Y. Effectiveness of ear splint therapy for ear deformities. Ann Rehabil Med. 2017; 41(1):138-47.
- Woo T, Kim YS, Roh TS, Lew DH, Yun IS. Correction of congenital auricular deformities using the ear-molding technique. Arch Plast Surg. 2016; 43(6): 512-7.
- Mohammadi AA, Imani MT, Kardeh S, Karami MM, Kherad M. Non-surgical management of congenital auricular deformities. World J Plast Surg. 2016; 5(2): 139-47.
- Esteves SDS, da Silva AP, Coutinho MB, Abrunhosa JM, e Sousa CA. Congenital defects of the middle ear - uncommon cause of pediatric hearing loss. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; 80(3): 251-6.
- Storck K, Staudenmaier R, Buchberger M, Strenger T, Kreutzer K, von Bomhard A, et al. Total reconstruction of the auricle: Our experiences on indications and recent techniques. BioMed Research International, vol. 2014, Article ID 373286, 15 pages, 2014.
What are Ear Deformities?
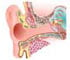
Ear deformities are defects of the ear. Ear malformations are caused by nearly half the defects in the nose, throat and ear. The ear consists of the outer, middle, and inner ear. The right ear is predominantly affected with deformities in the outer and middle ear. The inner ear could be affected in either one (unilateral) or both ears (bilateral). Deformities in the ear affect between 15 to 55 percent of children around the world. Occasionally, all three parts of the ear are affected with malformations. In other instances, only the outer and middle ear is affected (atresia auris congenita).
What are the Causes of Ear Deformities?
There are different causes of ear deformities that are listed below:
- Genetic syndromes: These include syndromes, such as Crouzon syndrome, Velocardiofacial syndrome, Down syndrome (trisomy 21), CHARGE (coloboma, heart defects, atresia choanae, growth retardation, genital abnormalities, and ear abnormalities) syndrome, and Goldenhar syndrome (oculo-auriculo-vertebral syndrome), which can cause ear deformities with functional defects. These account for 25 percent of middle ear malformation cases.
- Genetic mutations: These are observed in genetically-associated ear defects. Spontaneous genetic mutations may explain non-syndromic (atresia auris congenita) ear defects.
- Infections during pregnancy: These include viral infections such as influenza and rubella (German measles).
- Agents that affect development during pregnancy: Metabolic conditions, such as diabetes; chemicals, changes in pressure, exposure to noise, malnutrition, exposure to radiation, low oxygen, anti-epilepsy medications, vitamin A deficiency, and high doses of retinoic acid.
- Hormones: Deficiency of thyroid hormone not only causes ear deformities, but can also cause severe cognitive dysfunction and deafness.
- Alcohol: Alcohol consumption during pregnancy can cause various congenital deformities, including ear deformity.
- Smoking: Smoking during pregnancy can lead to ear deformities, amongst others.
- Chemical agents: Thalidomide is a teratogen, which can cause multiple fetal deformities, including that of the ear.
- Family history: A family history of ear deformities significantly increases the chances of a child being born with ear deformity.
- Trauma: In rare situations, trauma or other accidents can cause ear deformities.