- Japanese Encephalitis - (https://www.cdc.gov/japaneseencephalitis/qa/index.html)
- Herpes Meningoencephalitis - (http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/healthlibrary/conditions/nervous_system_disorders/herpes_meningoencephalitis_134,27/)
- Encephalitis - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001415.htm)
- Disease and Conditions - Encephalitis - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/encephalitis/basics/definition/con-20021917)
What is Encephalitis?
Encephalitis is defined as the inflammation and swelling of the brain.
- It is a rare, but life-threatening condition. It can affect persons belonging to any age group, but the very young and elderly are at the highest risk.
- The frequency of encephalitis is highest in the first year of life and subsequently decreases with age.
- Encephalitis often causes mild, flu-like symptoms such as fever, body ache, headache and fatigue. In some cases, it can be serious and life-threatening.
Types of Encephalitis
There are mainly two types of encephalitis:
- Infectious- Infectious encephalitis are also known as primary encephalitis. It occurs as a result of invasion of the brain by pathogens. The most common culprit is virus. Other organisms that can cause encephalitis are bacteria, parasites and fungi.
- Autoimmune- This type of encephalitis is caused when the immune system erroneously attacks the brain. This is called autoimmune encephalitis.
It has been estimated that globally, around 40% of encephalitis cases are infectious, 20% are autoimmune and around 40% are due to unknown causes.
What are the Causes of Encephalitis?
The two major causes are infectious and autoimmune. The disease process may involve large parts of the brain (diffuse) or a small area of the brain (focal). Very often there is associated inflammation of the membranes (meninges) covering the brain. When this occurs, it is referred to as meningoencephalitis.
Infectious Encephalitis- The most common infectious agents causing encephalitis are viruses followed by bacteria and fungi.
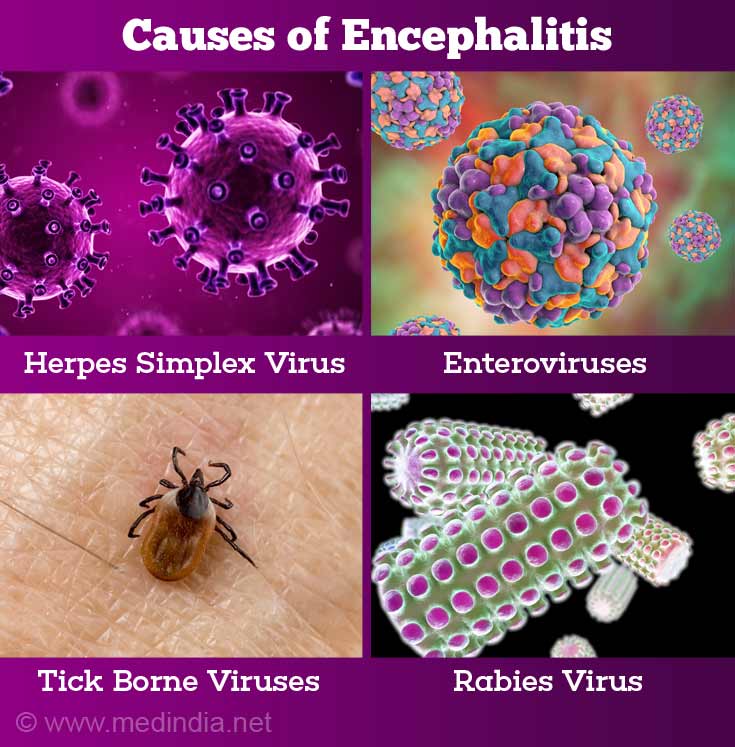
Viral - The most common viruses that cause encephalitis include the following:
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV) - This virus is normally responsible for cold sores (HSV-1) or genital herpes (HSV-2). Though rare, herpes infection can be complicated by encephalitis.
- Other herpes viruses - The varicella zoster virus (VZV) which causes chicken pox and shingles and the Epstein Barr virus (EBV) responsible for infectious mononucleosis can also cause encephalitis.
- Enteroviruses - Polio virus, an enterovirus can also involve the brain. However, this is rare nowadays due to eradication of the disease in most parts of the world by successful vaccination programs.
- Childhood illness - Infections such as measles, mumps and rubella (German measles) can be complicated by encephalitis. Fortunately, successful vaccination programs have reduced the incidence of these diseases globally.
- Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) - This virus is transmitted by mosquito bites. It is seen mostly in the rural parts of Southeast Asia, The Far East and the Pacific Islands. It is more common in children under 15 years. Vaccines are available to protect against the disease.
- Rabies virus - It is transmitted by the bite of an infected animal such as dog and causes rabies. With onset of symptoms, there is rapid progression. However vaccines are available to prevent the disease in persons working with animals and to prevent the disease following animal bites.
- Tick borne viruses - Rare cause of encephalitis eg Powassan virus encephalitis.
- HIV encephalitis - In some persons with HIV infection, the brain may become affected a few months following initial infection when the body’s immune system attacks the virus. Fortunately most persons recover with and sequelae.
Other Infectious Agents
Apart from viruses, bacteria, parasites and fungi can cause encephalitis.
These occur in rare proportions mainly in immunocompromised individuals, like those who have AIDS, those undergoing chemotherapy or taking drugs to prevent rejection following transplantation and people who have certain diseases that reduces their ability to fight disease.
Autoimmune Encephalitis
Autoimmune encephalitis occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the brain. This immune response is known as autoimmunity and it can lead to destruction of healthy tissue in the body.
This type of autoimmune reaction may be triggered by the following factors:
- Viral infection in the body that occurred a few weeks earlier (post-infectious encephalitis)
- Cancer in any part of the body
- Post-vaccination – in very rare cases
- Unknown
What are the Symptoms of Encephalitis?
Viral encephalitis can cause no symptoms or mild flu-like symptoms like:
- Fever
- Headache
- Malaise and fatigue
- Confusion
- Irritability
Severe cases of encephalitis can result in more serious symptoms and complications like:
- Seizures
- Hallucinations
- Muscle weakness or paralysis
- Loss of sensation in certain body parts or face
- Speech and hearing -related problems
- Loss of consciousness
- Vision-related problems
In some cases, following recovery, there may be some residual impairments such as paralysis, visual and hearing defects that have to be followed up and treated as appropriate.

How do you Diagnose Encephalitis?
History and Physical examination - A detailed history and physical examination may raise a suspicion of encephalitis. The physician conducts laboratory tests and imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine the underlying cause.
Lab tests - Testing the blood, urine, throat swab or other body fluids, can help detect infections caused by viruses or other pathogens.
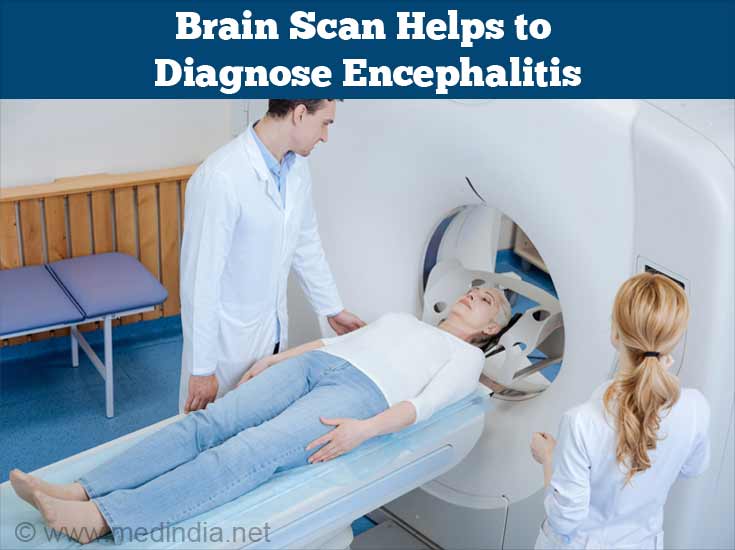
Brain Scan - A brain scan helps rule out encephalitis or any other problem like brain aneurysm, which is a swelling in the artery or blood clot, a tumor or any other cause.
Types of diagnostic imaging commonly employed include:
CT scan - several X-rays are taken from different angles and are put together by a computer to create a detailed image of the brain
MRI scan - strong magnetic fields and radio waves are used to produce a detailed image of the brain
Lumbar puncture or Spinal tap - It is procedure of removing the fluid around the spinal cord known as cerebrospinal fluid, to check for signs of encephalitis. For the procedure, the patient lies on his/her side and pushes the knees up to the chin. The lower back is numbed using a local anesthetic and a needle is inserted in to the lumbar part of the spine to extract the fluid. The sample is then analyzed in the lab for signs of infection or some immune system dysfunction.
Electroencephalogram (EEG) - While performing an EEG a series of small electrodes are attached to the scalp. The electrodes, pick up the electrical signals and record the electrical activity of the brain. It helps to detect any abnormal patterns, which may be consistent with a diagnosis of encephalitis.
Brain biopsy - In this procedure, a small sample of the brain tissue is removed. This is rarely performed and is only indicated if the patient does not respond to treatments or if symptoms worsen.
How do you Treat Encephalitis?
Basic management of encephalitis includes:
- Treating the underlying cause
- Offering symptomatic relief
- Support of vital body functions
Mild cases of encephalitis can be treated by ensuring adequate bed rest, taking plenty of fluids and using some anti-inflammatory drugs like acetaminophen, ibuprofen and naproxen sodium, to relieve headaches and fever. Severe cases require urgent attention, warranting hospital admissions in the intensive care unit (ICU).
Treating the Cause
Treatment can be started immediately on identifying the underlying cause.
- Antivirals - Most cases are caused by viruses and the use of antiviral medications like Acyclovir and Ganciclovir, can be helpful. For viruses that cause chicken pox and herpes, intravenous injections using antivirals are required .

- Steroids - If immunity plays a role in triggering encephalitis, then steroid injections are advised.
- Immunoglobulin therapy - This is recommended if steroid injections, fail to control the immune system.
- Antibiotics or Antifungal medication - These are used if encephalitis is caused by a bacterial or antifungal infection.
Symptomatic Management and Supportive Treatment
- Intravenous fluids-To manage symptoms of dehydration and maintain a balance of essential minerals, fluid can be replaced intravenously.
- Anti-pyretics and Analgesics- Fever, swelling and headache can be managed using anti-inflammatory drugs like Ibuprofen or Acetaminophen.
- Anti-convulsants- In severe cases, that causes seizures, medications like phenytoin, can be used.
- Relaxants-If the person is very agitated, certain relaxants can be prescribed.
- Surgery- Very rarely, if there is a build of pressure in the brain, a surgery to remove the pressure may be needed, especially if the medications do not work.
- Breathing Assistance-Oxygen can be given through masks, to support the lungs and a ventilator can be used to control breathing.
Long-term Management of Complications
Depending on the severity of the illness and the symptoms, additional therapy maybe needed. These include:
- Physiotherapy - To improve the strength and flexibility of muscles. To help maintain balance, motor coordination and improve motility.
- Speech therapy -In some cases where encephalitis causes speech related problems, speech therapy helps to relearn muscle control and coordination to produce speech.
- Psychotherapy -Can be useful to address personality changes or improve mood disorder.
- Occupational therapy - Helps to develop skills needed for everyday activities.
How do you Prevent Encephalitis?
The best way to prevent viral encephalitis is through:
- Vaccinations - Routine vaccinations against childhood infections like measles and rubella should be administered.
- Good hygiene practice - Regular washing of hands before and after meals.
- Avoid contact with active cases - It is important to avoid contact with anyone who is infected.
To prevent cases of Japanese encephalitis, vector control is imperative. Mosquitoes and ticks are important vectors and exposure can be minimized by:
- Wearing protective dressing
- Use of mosquito repellent on both skin and clothes
- Get rid of stagnant water sources both outside and inside
- Vaccination of animal handlers and people working in pig farms

Health Tips
- Adopting healthy eating habits - to improve health of the immune system
- Vaccinations - ensuring that children receive all routine childhood vaccinations
- Protection from mosquitoes - this can be done by either wearing long sleeved-clothes or using insect repellents