- Facts about Encephalocele - (https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/encephalocele.html)
- Encephalocele - Rare Disease - (https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/encephalocele/)
- Encephalocele - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/encephalocele)
What is Encephalocele?
Encephalocele is a birth defect which occurs when the neural tube fails to close completely. The neural tube is a structure during the embryonic life which folds and closes to develop into the brain and spinal cord.
Encephalocele is a pedunculated or sessile cystic sac which is due to protrusion of brain through the abnormal gap in between the skull bones. They are located in the centre of the skull anywhere between the nose on the front side to the neck on the back. Encephaloceles are more common in the back of the head.
The sac is covered by skin or a thin membrane. When the sac contains meninges along with brain it is called meningoencephalocele. When the spinal cord is present along with brain it is called encephalomyelocele. If the sac has only meninges it is called meningocele.
An encephalocele can be classified as
- Primary (congenital) encephalocele: It is a congenital birth defect.
- Secondary encephalocele: It is an acquired defect in the skull which occurs due to the injury.
- Frontal or posterior: Depending on location.
Facts of Encephalocele
- It is seen 1 in 10,000 babies in the USA.
- In girls, it is more common on the back of the head.
- In boys, it is more common on the front side of the skull.
- In western countries, it is more common on the back of the head.
- In Southeast Asia, it is more common on the front side of the skull.
What are the Causes of Encephalocele?
- The exact cause is unknown.
- It is multifactorial according to many researchers. Both environmental and genetic factors are involved.
- It is observed in patients with family history of neural tube defects like spina bifida and anencephaly thus indicating genetic involvement.
- The environmental factors like teratogens may trigger in such cases and lead to encephalocele. Trypan blue and arsenic are teratogens which can cause damage leading to abnormal fetal development and encephalocele.
What are the Symptoms and Signs and Complications of Encephalocele?
Encephalocele is usually associated with craniofacial abnormalities. The following symptoms may be present in patients with encephalocele
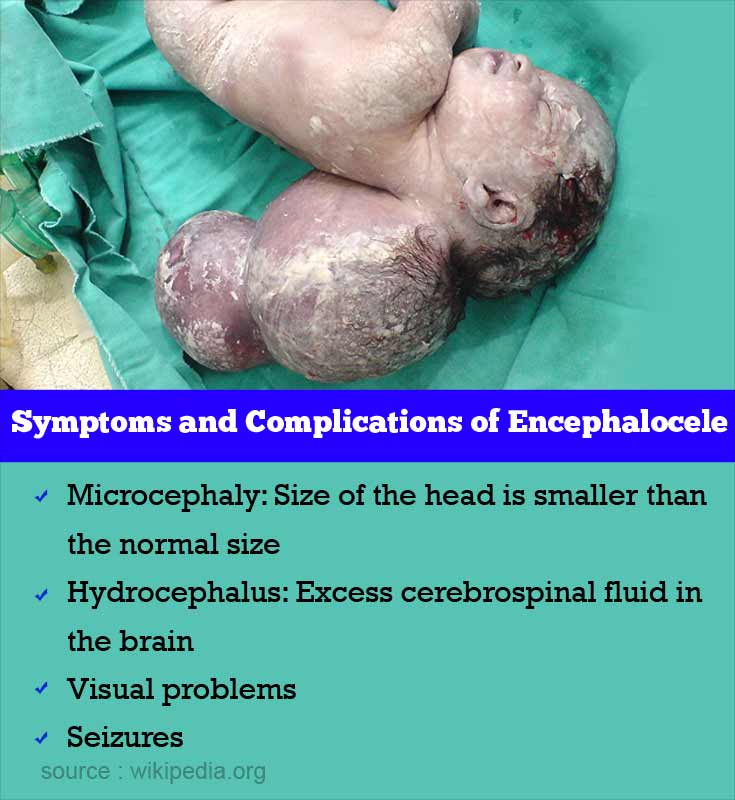
- Microcephaly: Size if the head is smaller than the normal size.
- Hydrocephalus: Excess cerebrospinal fluid in the brain with an increase in the pressure of the brain.
- Visual problems
- Seizures
- Pain near the encephalocele
- Swallowing and breathing difficulties
- Delayed milestones
- Mental retardation
- Growth retardation
- Spasticity
- Ataxia: It is a neurological sign, where the muscle coordination is lost and the voluntary movement is affected.
How do you Diagnose Encephalocele?
Postnatal Diagnosis
The diagnosis of encephalocele can be made easily in the newborn because mostly it is an obvious swelling except in a few very cases.
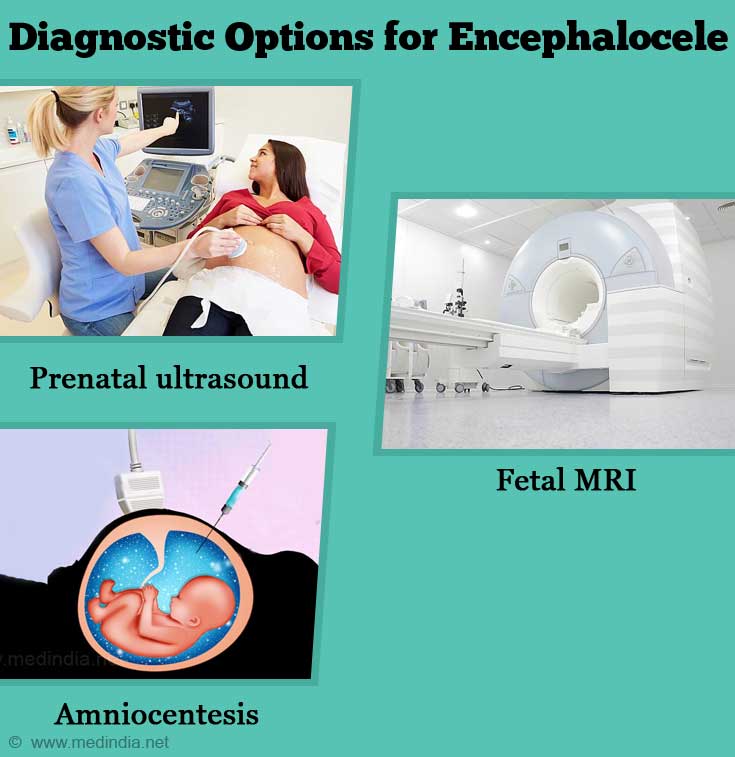
Prenatal Diagnosis
The diagnosis of encephalocele can also be made prenatally by
- Prenatal ultrasound: Ultrasound of abdomen and pelvis in a pregnant women helps to detect the encephalocele.
- Computerized Tomography (CT): It is an imaging technology which helps to detect the extent of the lesion.
- Fetal MRI: Fetal MRI can also help to detect encephalocele. It also helps to identify the contents of the sac and to find if there are any associated anomalies. It helps in planning the best treatment.
- Amniocentesis: When fetal encephalocele is found on ultrasound, amniocentesis helps to find any associated chromosomal anomalies in the fetus.
How do you Treat Encephalocele?
MODE OF DELIVERY
When the encephalocele in the fetus is diagnosed before pregnancy, if its size is small vaginal delivery can be performed. In case of a larger encephalocele, a caesarean section may be required to deliver the baby.
SURGERY
Surgical repair is the available effective treatment of encephalocele. The treatment is provided during infancy usually between birth and four months of age. When the encephalocele sac is covered by skin, the treatment can be delayed but if it is covered with membrane it requires immediate attention. The type and extent of repair depend on the size, site and the contents in the encephalocele.

Open surgery: To repair encephalocele, the skull is cut and open. Then the dura mater of the brain is cut, and then the herniated brain and meninges are relocated into the skull. Most often the brain tissue in the sac is abnormal which needs removal, but if the healthy tissue is present, it has to be preserved. The sac is removed. Then the dura layer is sutured and the skull is closed.
In cases with associated hydrocephalous surgery may be required to relieve the intracranial pressure by ventriculo-peritoneal shunts. The associated craniofacial deformities need correction.
The treatment goals are
- To close the skin defects to avoid the desiccation and infection of the brain.
- Remove the nonfunctioning extracranial tissue with a good closure of the dura.
- Craniofacial reconstruction.
Endoscopic endonasal approach (EEA): It is a minimally invasive procedure, where the surgeon accesses the encephalocele through nose and nasal cavity. The benefits of this procedure include
- No skin incisions to heal
- No disfigurement of the face
- Quick recovery
Prevention of Encephalocele
Administration of 400 micrograms of folic acid in women planning for pregnancy is recommended.
Prognosis of Encephalocele
- An encephalocele without the brain in the sac is associated with good prognosis.
- Frontal encephalocele is associated with a better prognosis than posterior encephalocele.
- The factors which lower the survival rates in infants with congenital encephalocele are
- Preterm birth
- Low birth weight
- Associated multiple defects
- Black/African Americans









