Q: Which doctor should I consult for this condition?
A: You should visit your gynecologist, who will order the necessary tests, and if required, ask you to consult a neonatologist after the birth of your baby.
Q: When should I consult a doctor?
A: Before birth:
- If you feel that your baby is moving less or not moving at all;
- If you develop a fever.
- If your baby develops a fever;
- If your baby develops jaundice. In any of these circumstances, you should immediately see a doctor.
Q: What is hemolytic disease of the newborn?
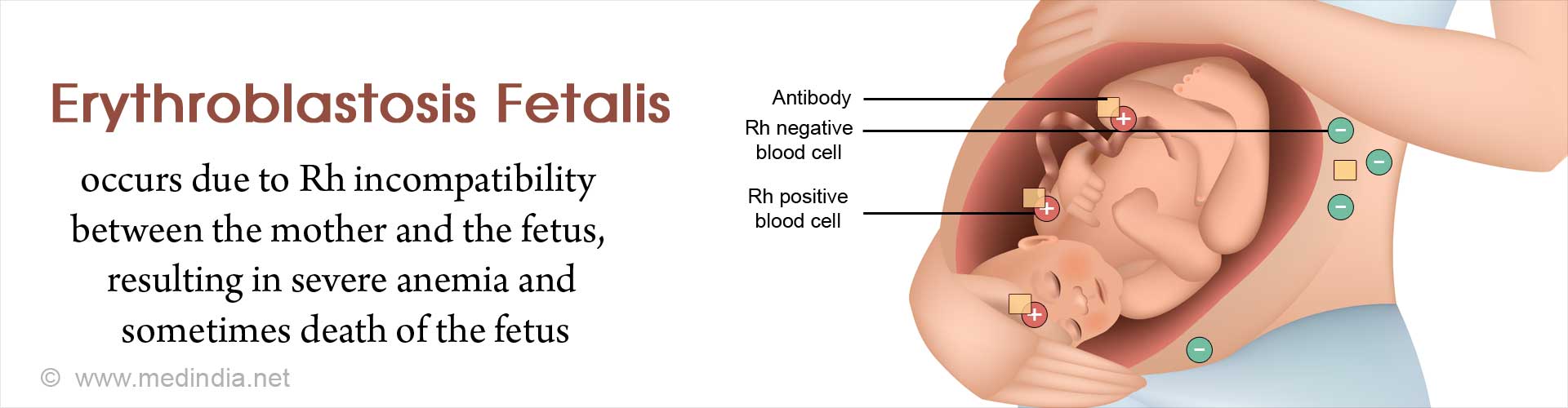
A: Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) is another name for erythroblastosis fetalis. This condition occurs due to the transfer of IgG type of anti-Rh antibodies produced by the mother through the placenta. These antibodies attack and destroy the baby’s RBC.
Q: What is isoimmunization?
A: It is the production by an individual of antibodies against constituents of the tissues of another individual of the same species. In the context of erythroblastosis fetalis, this occurs when fetal RBCs, which possess an antigen that the mother lacks, are transferred transplacentally, and elicit antibody induction in the mother’s body. Subsequently, the antibodies return to the fetus by the same route, resulting in RBC lysis.
Q: What should I do to ensure that my baby is out of danger?
A: You should visit your neonatologist regularly for at least 3 to 4 months to monitor for signs of anemia. If required, further blood transfusions may be given. With proper care, your baby should have no further complications.
Q: Why autoimmune hemolytic anemia is also called Coombs disease?
A: Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is a rare disease in which antibodies are made against a person’s own RBCs. It is also known as Coombs disease because two blood tests can check for antibodies that attack RBCs. These are the direct Coombs test and the indirect Coombs test.