- Esophageal disease - (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/esophageal_disease)
- Esophagus Disorders - (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/esophagusdisorders.html)
About
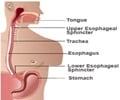
Esophagus is the tubular structure that carries food, liquids and saliva from mouth to the stomach. Functional esophageal disorders are health conditions that manifest typical esophageal symptoms such as heartburn, chest pain, globus and dysphagia. Sadly, most of these disorders are diagnosed as gastroesophageal reflux disease, especially if reflux esophagitis or excessive esophageal acid exposure is present.
Diseases of the esophagus are common but lack a well-defined pathogenetic mechanism and for this reason treatment remain empirical. Many people occasionally experience a burning sensation in their chest, also known as “heart burn”, which is caused by the acid in the stomach refluxing into the esophagus. If this happens for a long period the lining of the esophagus begins to erode, leading to Barrett's esophagus which is considered to be a precursor to adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Another common esophageal condition is the globus esophagus, in which a person feels as if a ball is lodged in the lower part of the esophagus.
Diagnosis of esophageal condition is primarily carried out by endoscopy although specific tests may be ordered according to the requirement. In the majority of the conditions, treatment focuses on reducing the symptoms and providing relief. Towards this end, the primary therapeutic approach is to administer oral medications and to bring about lifestyle changes. Surgery is done only if every other mode of treatment fails to bring relief.
A few diseases that affect the esophagus are described below:
Achalasia - This is a condition in which the esophageal motility is affected. Medications like calcium channel blockers and nitroglycerin, that help to relax the lower esophageal sphincter, are initially administered but durable relief is often brought about after a surgical procedure only. Surgical options involve a laproscopic procedure known as Heller myotomy, which is done to permanently open up a lower esophageal sphincter.

Esophagitis - This is a condition characterized by inflammation, irritation or swelling of the esophagus. Symptoms include swallowing difficulty and chest pain. Treatment for esophagitis depends on the underlying cause and, if left untreated, can lead to esophageal dysfunction.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) - This occurs when a muscle at the tip of the esophagus refuses to close properly, causing the contents of the stomach, including acid, to regurgitate back into the esophagus causing heartburn. Not all patients with GERD present with heart burn. Some can taste a liquid at the back of their mouth. If these symptoms are experienced even twice a week you may be having GERD. Other symptoms include dry cough, breathing difficulty and swallowing difficulty. GERD has to be treated to avoid complications. In patients experiencing early stages GERD lifestyle changes such as mentioned below can help to bring about relief-
- Wear loose-fitting clothes
- Avoid chocolate, peppermint, beverages and alcohol
- Avoid spicy and oily foods
- Eating smaller meals instead of three large meals
- Do not eat close to bedtime
- Tackle Obesity
- Manage Stress

Certain foods and pregnancy can cause heart burn. In some people, heart burn can be a prelude to heart attack. Seek immediate medical help.
GERD is diagnosed with endoscopy. In some cases a biopsy may be taken for microscopical evaluation.
Treating GERD and heart burn is absolutely necessary. GERD medications include antacids, histamine antagonists, pro motility drugs and proton pump inhibitors. In some cases, a surgery (fundoplication) is done to prevent reflex. This is very effective in relieving symptoms of GERD.
Complications (in 10% of those with GERD) can lead to Barrett’s esophagus, in which the esophageal lining gets eroded and could potentially lead to adenocarcinoma.
Cancer of the esophagus is a potentially fatal condition of the esophagus. It can occur anywhere along the esophagus but is mostly seen to occur in the lower part. Difficulty in swallowing, weight loss and coarse cough are prominent symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment helps to increase survival rates. Those with Barett’s esophagus must be regularly screened for cancer. Diagnosis is carried out through endoscopy and biopsy. Treatment methods usually consists of a combination of radiation and chemotherapy. Surgery is another very effective treatment option.