- Joseph King Ching Tsui: Blepharospasm
- Walsh & Hoyt’s Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology
About
Eye twitching or Blepharospasm, can last for a few hour or days and disappear spontaneously but sometimes it can persist and become a chronic problem and requires treatment.
The term Blepharospasm has its origin from Greek word – Blepharo which means eyelid and spasm which means uncontrolled muscle contraction or twitching.
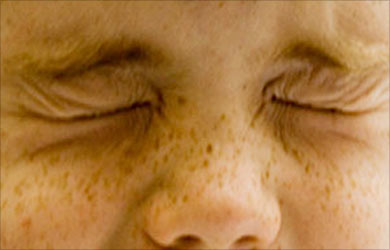
The medical term blepharospasm is more a general term that is applied to any abnormal blinking or eyelid twitch resulting from any cause, ranging from dry eyes to Tourette's syndrome to tardive dyskinesia. Eye twitching or Blepharospasm referred in this article is officially called benign essential blepharospasm (BEB) to distinguish it from the less serious secondary blinking disorders. The eye twitching in this condition is involuntary and occurs spontaneously every few seconds making it annoying and uncomfortable.
Blepharospasm is considered a benign condition. ‘Benign’ indicates the condition is not life threatening and "essential" is a medical term meaning ‘of unknown cause’. It is both a cranial and a focal dystonia. Cranial refers to the head and focal indicates confinement to one part. The word dystonia describes abnormal involuntary sustained muscle contractions and spasms.
Essential or primary blepharospasm refers to those patients whose condition has no obvious underlying cause. Secondary blepharospasm may result from drug, encephalitis, Parkinsonism and Wilson’s disease.
Onset is typically gradual. Initially blinking may increase in response to bright light, accompanied by sensation of eye irritation. Progression of symptoms affects the patient’s daily activities.
Diagnosis is based on a careful history and sometimes complete neurological examination.
There are a few conditions that resemble blepharospasm like Tics, Hemifacial spasm and Ptosis
They need to be ruled out by appropriate history taking and examination by the clinician.
Tablets have been used to treat blepharospasm. If it is chronic then Botulinum toxins injections should be considered for its treatment. Surgery is usually done when the patient does not respond to Botulinum injections.