About
Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a disease of the bones characterized by abnormal growth areas or lesions in one or more bones where normal bone is replaced with fibrous bone tissue.
Fibrous dysplasia is condition with abnormal growth areas in one or more bones, where normal bone is replaced with fibrous bone tissue. Though any bone in the body can be affected with fibrous dysplasia, the most commonly affected bones are -
- Skull/jaw bone/facial bones- 46%
- Bones of the lower limbs- 45%
- Bones of the upper limbs- 6%
- Ribs/spine/clavicle- 3%
Usually a single bone is affected, with the condition known as monostotic fibrous dysplasia; when multiple bones are involved, it is known as polyostotic fibrous dysplasia.
The exact cause of fibrous dysplasia is not known.
The fibrous bone gradually grows and expands, causing a weakened area of the bone. This area of weak bone can cause pain. It can fracture the bone and may lead to deformity.
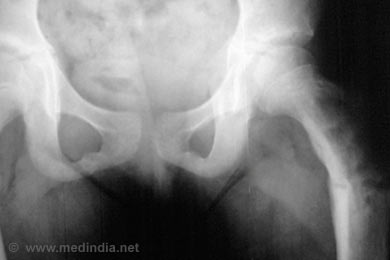
Fibrous dysplasia of the bone can be diagnosed with routine imaging tests like X-ray or MRI. Most cases are diagnosed in adolescence and young adulthood and remain unchanged throughout life. The initial manifestations of fibrous dysplasia are most commonly found in persons aged 3-15 years.
Fibrous dysplasia is curable only if there is one lesion in a bone and that lesion is completely eliminated by surgery. But most of the times, there are unidentified fibrous dysplasia cells in several bones and it is not possible to eliminate all these cells by surgery.