About
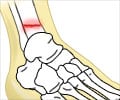
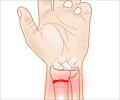
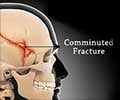
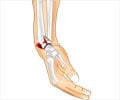
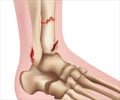
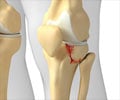
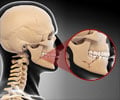
A fracture is a condition where the continuity of a bone is lost.
Majority of bone fractures occur because of high force impact or stress on a bone. However, a fracture may also be the result of some underlying medical conditions which weaken the bones, for example osteoporosis and some cancers. The risk of fracture increases as weage because, in old age, our bones can withstand less force.
The signs and symptoms of a fracture vary according to the affected bone and the severity of the injury. However, pain, swelling and difficulty of movement are the common symptoms.
Diagnosis of fracture includes a detailed history and physical examination. X-rays are often taken. Occasionally, CT scanor MRI is used to find the extent of damage to the bone and adjacent tissues.
Initial treatment for fractures includes splinting the affected area, elevation and applying icepack. Conservative treatment for fractures involves pain management and immobilization with plastic casts or metal screws. Immobilization is helpful with initial pain control. Surgical intervention is sought if conservative treatment fails or is not possible.