- Preferred Practice Patterns: Diabetic Retinopathy: American Academy of Ophthalmology
- Diabetic Retinopathy: All India Ophthalmological Society CME Series
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetes has the potential to affect different organs of the body including the eyes and most importantly the retina.
Retina is the nerve tissue at the back of the eye which is vital to the process of vision. The damage caused by diabetes to the retina is called Diabetic Retinopathy.
- Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is the fastest growing cause of blindness worldwide and the single most preventable cause of such blindness in the world.
- This has been due to the rising incidence of diabetes globally. The incidence of diabetes is five times the white population in some of the Asian Countries including India, China and some of the African Countries
- The data released by the International Diabetes Federation in the year 2020, estimates that there are around 463 million people affected by Diabetes worldwide of which 77 million are in India.
In India among the 77 million people with diabetes, an estimated 25 million are afflicted with Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) and 7 million with vision threatening DR but only 15,000 practicing ophthalmologists.
A survey report released by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in 2019 states the prevalence of diabetes in India is 11.9% in people above 50 years of age.
Prevention of vision loss from DR requires early detection via eye exams and regular screenings by a trained ophthalmologist. However, there are not sufficient specialists globally to screen everyone at risk.
What are the risk factors for the development of Diabetic Retinopathy?
The risk factor for development and progression of Diabetic Retinopathy are -
- Prolonged duration of the disease
- Uncontrolled blood sugar
- Presence of other associated diseases like high blood pressure & high cholesterol
- Presence of nephropathy or kidney related disease
- Pregnancy
How is Diabetic Retinopathy Classified?
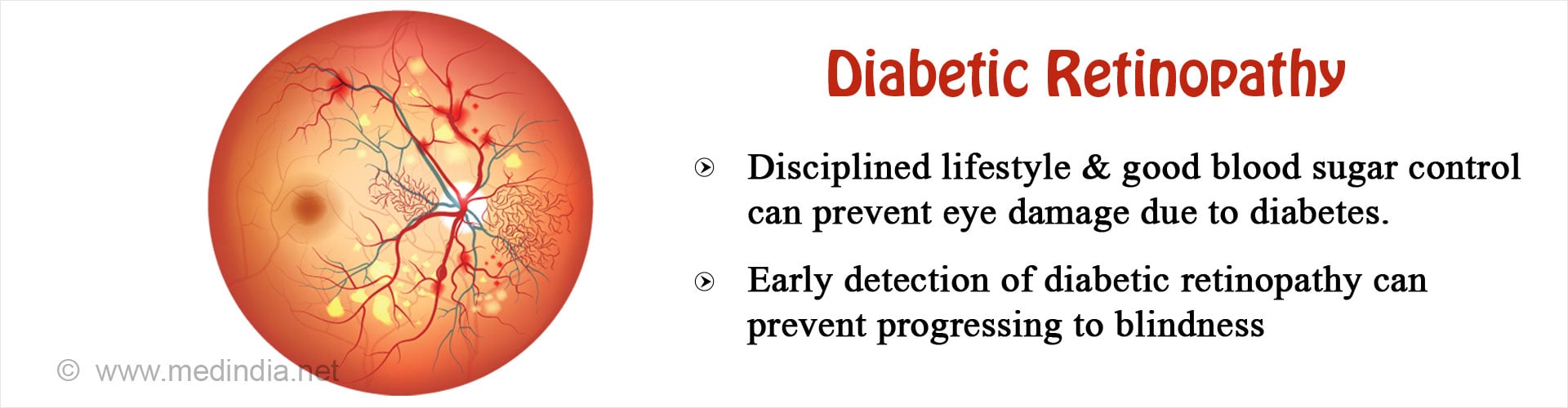
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Early stage of Diabetic Retinopathy or Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy - At this stage there maybe no symptoms but gradually as it progresses it leads to difficulty in vision. As the early stage may not be symptomatic, it is important that patients with diabetes should undergo regular checks of their eyes and the retina (once a year) to ensure early detection and intervention to prevent vision loss. The findings on the retina are as follows -
- The excess blood glucose gets deposited in the walls of the small blood vessels of the retina and distorts their normal architecture. This causes the blood vessels to become swollen and leaky. The swollen blood vessels are called microaneurysms.
- Lipids and proteins from the blood leaks out of these blood vessels and get deposited in the retinal tissue resulting in thickening or swelling of retinal tissue. These are called hard exudates.
- When this swelling occurs in the central and most important part of the retina called macula, it is called Diabetic Macular Edema
- Some blood vessels may also rupture resulting in hemorrhages in the retina.
1. Advanced stage of Diabetic Retinopathyor Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy – Progression of the problem leads to this stage and can result in complete vision loss or blindness. The features include:
- There is decrease in the blood flow through the small retinal blood vessels. Thus, the retina starts becoming hypoxic or oxygen starved. In response to this, a mediator called Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) increases in the retina. This mediator causes new vessels to start appearing in the retina with the aim to bring in more oxygen.
- These new blood vessels are often fragile and abnormal. They rupture and bleed causing accumulation of blood in the space in front called vitreous cavity leading to vitreous hemorrhage.
- The end stage of the disease is characterized by retinal detachment or separation of retina from the eye wall and leads to irreversible vision loss
What are the other effects of Diabetes in the Eye?
Apart from this, diabetes also increases the risks of blood vessel getting blocked in the retina leading to Stroke in the Eye (Central Retinal Artery or Vein Occlusion). Early development of Cataract (Clouding of the lens of the eye) and Glaucoma (Increased eye pressure) are other eye diseases having a strong association with Diabetes.
What are the Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy?
- It is generally not symptomatic in the early stages
- Gradually progressive decrease in vision is the most common complaint. One eye may be more affected than the other
- Sudden and severe loss of vision may be seen in advanced stage of Diabetic Retinopathy if there is vitreous hemorrhage

How is Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosed?
It is diagnosed by examination of the retina by an ophthalmologist after dilatation of the pupil with dilating eye drops.
What are the investigations advised for Diabetic Retinopathy?
- Fundus Fluorescein Angiography (FFA) - This is a procedure to study the blood vessels of the retina and ascertain the stage of Diabetic Retinopathy. A dye is injected into the patient’s vein and photographs of the retina are taken with a special fundus camera during the passage of the dye through the retinal blood vessels.
- Optical Coherence Tomography - This is a scan of the retinal layers using infra-red rays. It is used to evaluate Diabetic Macular Edema.
How can eye damage due to diabetes be controlled or treated?
Management of Diabetic Retinopathy
- Regular eye examination, at least once a year by an ophthalmologist is a must for all patients affected with Diabetes even in the absence of any visual complaints. As it was mentioned earlier, diabetic retinopathy is relatively symptom free in the early stages and causes visual complaints only in the advanced stages. So regular screening of diabetic patients is very important for early detection and management of Diabetic Retinopathy.

- Strict control of blood sugar and other associated comorbidities like hypertension, high cholesterol is advised in the early stage or Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
- Laser photocoagulation of retina also called Panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) is advised when Diabetic Retinopathy advances towards the proliferative stage. Multiple sittings of treatment are usually required
- Injection of anti-VEGF drugs into the vitreous cavity is done to reduce proliferation of new blood vessels
Surgical treatment: Advanced procedures like Pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) may be needed in cases which are not responding to other forms of treatment.