- Bunions - (http://www.foothealthfacts.org/footankleinfo/bunions.htm)
About
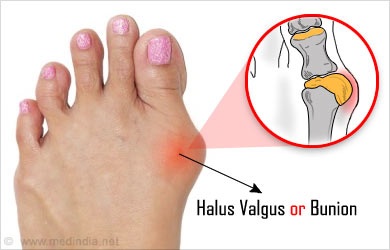
Halus Valgus or bunion is a bump on the side of the big toe. Actually, this deformity is more than a bump as it indicates changes in the bones in the front of the foot.
In a person with bunion the big toe does not face forward but leans towards the second toe. This impairs the alignment of the bony framework of the foot leading to the ‘bump.’ Bunions are often wrongly described as bone or tissue growth around the toe.
Also, medical professionals are not in agreement with each other regarding the causes of bunion. Some believe that there is a genetic cause while others attribute the deformity to long-term use of ill-fitting or tight, pointed shoes. There may be some truth in these opinions as bunions are not commonly found in people in whose cultures wearing shoes is not mandatory.
Bunions are progressive and usually occur when pressure is applied to the side of the big toe forcing it under, over or towards other toes. This process, known as angulation, occurs over the years causing a bony deformity on the metatarsophalangeal joint of the toe, giving rise to the characteristic ‘bump’. Symptoms appear late and in some, they do not manifest at all.
Causes
Bunions are mostly seen to occur in those who have inherited a faulty foot structure. Some people with a certain foot type are predisposed to bunion. Wearing shoes on an everyday basis accelerates the deformity, makes symptoms to appear faster and progressively worsens the condition.
Arthritis of the big toe joint, diminished and/or altered range of motion and discomfort, with pressure applied to the bump or with motion of the joint, may all accompany bunion development. A bursa can arise atop the first metatarsal, head either medially or dorso-medially. When this bursa becomes inflamed (bursitis), it can cause a lot of pain.
Symptoms
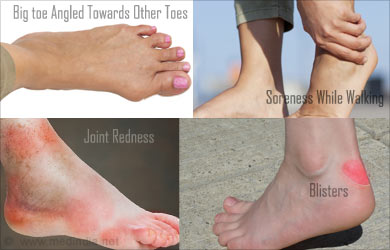
Symptoms of bunion include:
- Big toe angled towards other toes
- Inflammation or irritation around the bunion
- Joint redness
- Pain or soreness while walking
- Burning sensation
- Numbness
- Blisters(occasionally)
Mostly, symptoms are seen to manifest while wearing ill-fitting shoes, pointed or high-heeled shoes and for this reason bunion is more common in women in comparison to men. Standing continuously for long periods aggravates the symptoms.
When the deformity becomes more severe the foot can hurt even while wearing loose shoes as the condition would have transformed into a functional impairment of the foot.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Bunions are easily visible to the naked eye and a physical exam is sufficient to establish diagnosis. However to confirm and completely evaluate the degree of deformity, X-rays may be recommended.
There are so many misconceptions about the condition and very often people do not take medical help on time. Bunions are progressive and are likely to worsen with time. Once complete evaluation is done the health care expert may come up with a treatment plan that is best suited for the patient.
Symptoms of halus vagus may be addressed through rest, ice packs, medications and different orthotic measures. These steps may alleviate the symptoms for a while but are not adequate to correct the problem. Surgery, by an orthopedic surgeon or a podiatric surgeon may be necessary if the deformity is severe.
Non-Surgical Treatment
In some cases, observation and periodic evaluation of the bunion is all that is required to reduce damage to the joint and manage the deformity. In many cases, treatment is required to relieve pain. Some treatment methods are mentioned below-
- Wearing right shoes is very important in controlling pain caused by bunion. Avoid pointed, ill-fitting and high- heeled shoes. Always wear shoes with a wide toe box
- Padding - Pads that can be placed over the area of the bunion can be purchased at a drug store. These help to minimize pain
- Changes in Activity - Avoid activities that causes pain, such as standing for extended periods of time
- Medications - Use of oral non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen may help to reduce pain and inflammation
- Icepack - Applying an ice pack over the area of the bunion many times a day helps to reduce inflammation and pain

- Injecting corticosteroids - This method is useful in treating an inflamed bursa (fluid-filled sac near around a joint) that may be seen with the bunion. However this method of treatment is very rare
- Orthotic devices - Sometimes orthotic devices are provided by the doctors to help the patient deal with the symptoms of bunions. They include
- Gelled toe spacers
- Bunion / toes separators
- Bunion regulators
- Bunion splints
- Bunion cushions
A variety of orthotics including over-the-counter or off-the-shelf commercial products and customized orthotics are also available.
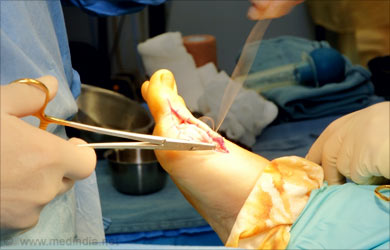
Surgery
Surgery is a permanent solution to this painful deformity and is considered when non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief or when the symptoms of bunion interfere with the daily activity of the person. A surgery is usually carried out to address the various pathologies that are responsible for the condition. Some of the common steps involved in surgery include
- Removing the abnormal bony enlargement of the big toe ( first metatarsal )
- Realigning the first metatarsal bone relative to the bones of the adjacent toes
- Straightening the big toe relative to other toes
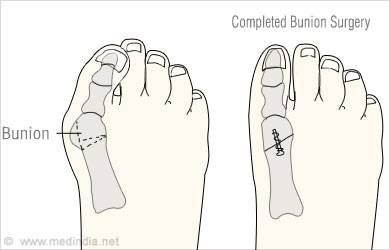
- Realigning the cartilagenous surfaces of the joint of the big toe
- Correcting arthritic changes of the big toe joint
- Repositioning the sesamoid bones under the first metatarsal bone
- Shortening, lengthening, lowering or raising the first metatarsal bone
Other steps may also be carried out for different effects depending on the correction required, the age, health level, lifestyle and activities of the patient. The surgery is usually carried out under anesthesia and the patient is expected to recover within 6-8 weeks time. During the recovery period the patient can move around with the help of crutches. An orthopedic cast is outdated and it is common for surgeons to use hardware (including screws and absorbable pins) to stabilize and fix the bone.