Head Injury - Types
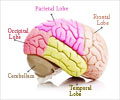
Head injury can be classified into different types based on the location and severity. The injury can be in one specific area of the brain (focal brain injury) or different regions of the brain may be injury of different parts of the brain) and severity of brain injury. It can range from a mild concussion to severe injuries, resulting in death of the affected individual.
When a person's head is subjected to external force, it can damage the superficial skin, skull, and / or the underlying brain. Small cuts, burns and bruising represent some forms of skin injury. It is not possible to comment upon the relation between skin and brain injury. A person with injured skin over his head may or may not have a brain injury. Similarly, a person with brain injury may not have an obvious skin injury.
Open And Closed Head Injuries
An external force exerted over the head can be sufficient enough to fracture or displace the skull. Under such an instance, a patient is said to have contracted an open head injury. It should be remembered that the term open injury is specific to the skull and does not relate to brain damage. In closed type of brain injury, there is no damage to the skull.
Based on type of force and amount of force, brain injury may be classified into different categories, as follows.
Concussion: It is the most common and minor form of head injury. Ideally, concussion refers to a temporary loss of consciousness in response to head injury. Of late, the term has also been used to describe a minor injury of the head or brain, as a consequence of change in movement or sudden momentum.
Contusion: Fracture of the skull can lead to a contusion. The skull is composed of bone tissue and protects the underlying brain. The inner surface of the skull is rough and hence friction caused due to movement of the brain within the skull can result in brain injury. Any bruising on the brain as a result of skull fracture is referred to as a contusion and represents a specific brain region of the brain that is swollen and mixed with blood from the damaged blood vessels.
Coup - Contrecoup Injury: This is also a form of contusion in which the impact of a brain injury is significant enough to affect the other side of the brain as well. Bruises are therefore present on either side of the brain. If the impact of the damage is severe enough, it can lead to neuronal damage (neurons are structural and functional units of the brain), resulting in a breakdown of communication among neurons.
Shaken Baby Syndrome: The condition can also occur as a response to back and forth movement of the brain, when a baby is shaken forcibly. This is commonly referred to as the shaken baby syndrome. The small size of the babies with respect to their relatively large head size in addition to lack of proper neck support and skull development can pose them at increased risk of this condition.
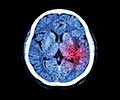
Hematoma: Damage of a blood vessel in the brain and the consequent heavy bleeding around the brain, leads to hematoma. Three different types of hematoma exist, based on the location of the bleeding, namely epidural, subdural and intracerebral hematoma.
Anoxia: Anoxia refers to brain damage as a result of complete reduction in oxygen supply to the brain tissue. However, the blood supply to the brain may be adequate. Hypoxia refers to a lack of proper oxygen supply to the brain. Starved of oxygen, cells in the brain die. This kind of brain damage is seen following drowning, heart attack or in people who suffer from heavy blood loss following extensive brain injury.
Second Impact Syndrome: This kind of a brain injury is seen when a person with brain injury sustains a second injury. It can happen either days or weeks following the first injury.