Glossary
Aortic stenosis: Narrowing of the aortic valve.Arrhythmia: Irregular Heart beat.
Asymptomatic: Absence of any symptoms.
Atrial Septal Defect: Hole in the wall separating the two upper chambers of the heart.
Cardiac Catheterization: A procedure in which a catheter is introduced into a blood vessel and guided into the heart in order to measure blood flow and evaluate structural defects.
Coarctation of aorta: Congenital narrowing of a segment of the aorta that impedes blood flow to the lower part of the body.
Congenital: Congenital is a term, which denotes Acquired by birth.
Cyanosis: Blue colored skin caused by too little oxygen in the blood.
Down’s Syndrome: A disorder caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21 and characterized by mental retardation and distinguishing physical features.
Echocardiogram: A procedure that uses ultrasonic waves directed over the chest wall to obtain a graphic record of the heart#$#s position, motion of the walls, or internal parts such as the valves.
Endocarditis: Inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, usually the heart valves; typically caused by an infection.
Heart failure: Condition caused when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body; also characterized by fluid collecting in various parts of the body (such as legs, lungs, liver).
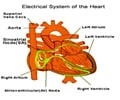
Interatrial septum: Wall separating the upper chambers of the heart or the atria.
Interventricular septum: Wall separating the lower chambers of the heart or the ventricles.
Palliative: Treatment undertaken not to cure but to improve a problem or condition.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus: A heart defect in which a fetal structure remains open, causing excess blood flow through the lungs.
Pulmonary Hypertension: Increased blood pressure in the arteries supplying blood to the lungs; caused by increased resistance to blood flow in the lungs, usually a result of a lung disease.
Pulmonary Stenosis: Obstruction of the flow of blood from the heart to the lungs.
Septum: A wall dividing two cavities or compartments.
Stroke: Sudden, severe attack that results in brain damage. Usually sudden paralysis or speech difficulty results from injury to the brain or spinal cord by a blood clot, hemorrhage or occlusion of blood supply to the brain from a narrowed or blocked artery.
Ventricular Septal Defect: Hole in the wall separating the bottom chambers of the heart or ventricles.