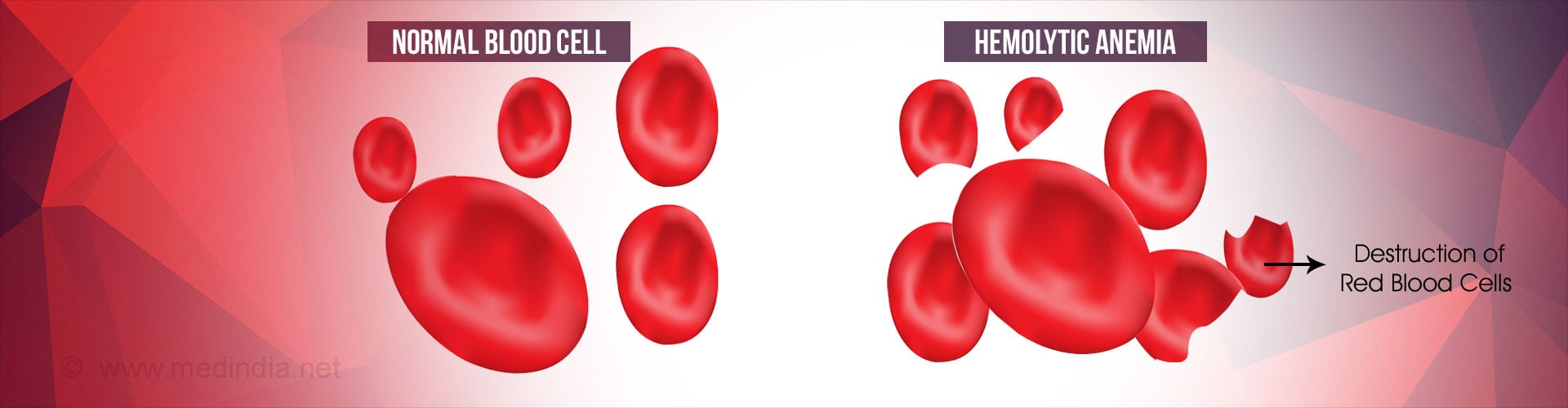
Glossary
Sickle cell anemia: A genetic disorder where the blood cells become sickle shaped when exposed to certain conditions like low oxygen levels and dehydration.Hereditary spherocytosis: A genetic disorder in which red blood cells are smaller, rounder, and more fragile than normal, causing hemolytic anemia.
Thalassemia: Thalassemia is a group of genetic blood disorders where the patient produces abnormal hemoglobin.
Lupus: Lupus is an autoimmune disease affecting body parts like the kidneys, skin, heart, joints and even the lungs.
Rheumatoid arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease of the connective tissues that usually appears in the form of painful swelling in the joints of the hands and feet. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) often worsens over time, causing joint deformities and disability.
Ulcerative colitis: A disease characterized by inflammation of the lining of the colon and rectum.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV): A virus that is a cause of severe pneumonia in people with a suppressed immune system, such as those undergoing bone marrow transplantation or those with leukemia or lymphoma.
Streptococcus: A common bacterium that causes disease like respiratory tract infections and skin diseases.
Leukaemia: Cancer affecting the white blood cells.
Lymphoma: A cancer of the immune system.
Reticulocyte: An immature red blood cell.
Bilirubin: A pigment formed from hemoglobin during destruction of red blood cell.